Exercises for various types of radiculitis. Radiculitis Charging for radiculitis
When the spinal cord nerve roots become inflamed, sciatica occurs. This is a common disease - up to 15 percent of the world's inhabitants suffer from this disease. This disease is getting younger - every year sciatica affects more and more young people. Like other diseases of the spine, sciatica affects people who place excessive stress on the spine, such as those who play professional sports, as well as those who move too little, such as office workers. To overcome lumbar radiculitis, you need to do therapeutic exercises.
Characteristics of the disease
The following causes of manifestations of inflammation of the nerves can be identified, of which there are not only many in the spine, but they play an important role in the functioning of human internal organs and the mobility of the limbs:

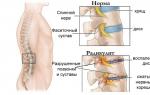
Radiculitis can be cervical, cervicobrachial, thoracic, and lumbosacral. Lumbar radiculitis is the most common; symptoms manifest themselves in severe back pain, which intensifies when walking and bending. During acute attacks, the pain can be unbearable, so drug therapy is used.
Treatment
If acute radiculitis pain occurs in the lower spine or in the neck area, you need to lie down in bed with a hard mattress, perhaps rub the sore spot with anesthetic ointment and keep your lower back warm, it is best to wrap yourself in a woolen scarf. It is better without painkillers, as they have many side effects, but if the pain is unbearable, then you can take a small amount of painkillers.
The doctor, as a rule, prescribes anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving medications, as well as for external use - warming ointments and rubbing liquids based on bee, snake venom, hot pepper, as well as B vitamins. After a couple of days of rest, active treatment begins. which, in addition to medications, includes physical therapy exercise therapy, therapeutic exercises, manual therapy, and massage. In extreme cases, surgery is possible, but only if the intervertebral disc has fallen out.
Principles of classes
When doing physical exercises, you must adhere to the following rules:

The purpose of therapeutic exercises:
- exercises are aimed at improving blood circulation and reducing congestion in the spine and surrounding tissues;
- the creation of a muscle corset leads to an increase in the gap between the vertebrae, which avoids compression of the nerve root, and improves nutrition of the nerve endings;
- restoration of tissue functions leads to improved motor functions and reduced pain;
- the spine becomes healthier and the risk of future diseases of this organ decreases.
 The preferred position is lying down, but you can sit or exercise squatting; in such positions the spine is not loaded. But in some cases, when a large load is needed, you can exercise while standing. At the initial stage, you need to relax the muscles of the shoulder, arms and back; after the movements are mastered, you can load these muscle groups, thus strengthening them. With lumbar radiculitis, it is also important to strengthen the abdominal muscles. If you feel acute pain, you should not bend or straighten your spine, as you cannot increase the pressure inside the spine.
The preferred position is lying down, but you can sit or exercise squatting; in such positions the spine is not loaded. But in some cases, when a large load is needed, you can exercise while standing. At the initial stage, you need to relax the muscles of the shoulder, arms and back; after the movements are mastered, you can load these muscle groups, thus strengthening them. With lumbar radiculitis, it is also important to strengthen the abdominal muscles. If you feel acute pain, you should not bend or straighten your spine, as you cannot increase the pressure inside the spine.
Contraindications - inability to move due to the severity of the situation and acute pain, heart problems. You need to start practicing with a physical therapy specialist under the supervision of your attending physician, because with the help of misunderstood therapeutic exercises you can not only recover, but also complicate your situation.
Exercises
Exercises are done lying on your back or stomach. The movements are suitable both as basic ones for lumbar radiculitis and as auxiliary ones for neck radiculitis. To achieve semi-bent legs, place a bolster under your knees. Repeat each exercise 10 to 15 times.
Therapeutic gymnastics will not only strengthen the muscles of the lumbar region, but also relieve inflammation, which is the main cause of pain in radiculitis. It is recommended to warm up before starting the exercises. Warm-up can be running in place or walking for 7-10 minutes. The gymnastics itself will not take more than 20 minutes.
As a rule, people suffering from these diseases perform a standard set of exercises. However, there may be exceptions depending on the course of the disease. In any case, it is not recommended to begin implementation without consulting this issue with your doctor.
Set of exercises
The standard complex is as follows:
- Lie on your back (on a hard, flat surface), bend your legs. Place your right hand along the body, your left hand on your stomach (or vice versa). Tighten your abdominal muscles. Hold them tense for a few seconds. Then relax. Repeat, keeping your hand on your stomach and using it to control tension and relaxation. 10 repetitions are enough. If you feel severe pain when doing this, straighten your legs so that the distance between your feet is approximately shoulder width. While performing this exercise, you should feel how your spine bends upward each time you tense your abdominal muscles.
- Continue lying down with your knees bent. Feet should be on the floor. Place your hands along the body. Without lifting your feet from the floor, raise your body and stay in this position for 5 seconds. After this, slowly lower your body to the floor. Repeat after a few seconds. Do 15 reps. In the future, you can complicate the exercise: instead of straightening your arms and positioned along your body, hold them behind your head.
- Lying on your back, straighten your legs and place your arms along your body. Bend your left leg and lift it so that it is 3-5 cm from the floor. Straighten your leg and slowly lower it. Then bend your right leg and do the same. Repeat 10 times (on each leg). After this, do it 10 more times, lifting 2 legs at the same time.
- In the same position, raise your legs above the floor so that in a raised position they are at a distance of 25-30 cm from the floor. Lock this position and remain in it for 5 seconds. Lower your legs, rest for a few seconds and repeat the exercise. Do 10-15 reps.
Also, the standard set of exercises includes the well-known “Bicycle” and “Scissors”.
These exercises are very simple to perform. To perform the “bicycle”, lie on your back, raise your legs, bend them at the knees and make movements with your legs, imagining that you are pedaling. In this case, your arms should be placed along the body and kept straight. “Scissors” is an exercise that is also performed while lying on your back. Raise both legs and make crossing movements without bending. In the initial stages, it is enough to perform this exercise 5 times, and then gradually increase the amount of movement to 15.
If you have sacral sciatica, the bridge exercise is very effective for treating this disease. To perform it you need to lie on your back. Straighten your arms and place them along your body. Raise your lower back so that your shoulder blades touch the floor (something like a regular gymnastics bridge). Stay in this position for 15 seconds. After this, lower your body to the floor, rest for a few seconds and repeat the exercise.
 It is also useful to perform the following exercise to treat this disease. Lying on your back, bend your knees and spread your arms to the sides and place them so that your palms touch the floor. Move your bent knees first to the left, trying to touch your knees to the floor, then to the right. Repeat 10 times in each direction (alternately).
It is also useful to perform the following exercise to treat this disease. Lying on your back, bend your knees and spread your arms to the sides and place them so that your palms touch the floor. Move your bent knees first to the left, trying to touch your knees to the floor, then to the right. Repeat 10 times in each direction (alternately).
Some exercises can be done standing. The standard package includes:
- raising and lowering the arms, accompanied by inhalation and exhalation;
- stepping from heel to toe and back;
- body tilts left and right.
The first exercise is very useful because it also includes breathing exercises. Stand up straight and while inhaling, raise your arms up. Stay in this position for a few seconds (hold your breath too) and lower your arms, exhaling. Repeat 5-10 times.
When performing the exercise, which involves stepping from heel to toe and back, your arms should be relaxed and lowered.
To perform bends, you need to stand straight. Hands on the belt. Feet shoulder width apart. Bend your left leg and tilt your body to the right. Then repeat the same with the other leg and in the other direction. Do 10 repetitions in total.
Another exercise should be performed while standing on all fours. As you inhale, stretch your neck forward and bend your lower back. As you exit, lower your head down, arching your back. Repeat 10 times.
 As you can see, the complex includes simple exercises that will not require you to make maximum efforts and strain very much. All exercises are performed sequentially, slowly. Some patients feel their effectiveness already on the 2nd day, while with more complex and advanced forms of radiculitis, the effectiveness will become noticeable only after a month of regular use. This complex is suitable for patients of any age. The entire complex must be performed daily, since otherwise it will be almost impossible to achieve the desired effect from gymnastics.
As you can see, the complex includes simple exercises that will not require you to make maximum efforts and strain very much. All exercises are performed sequentially, slowly. Some patients feel their effectiveness already on the 2nd day, while with more complex and advanced forms of radiculitis, the effectiveness will become noticeable only after a month of regular use. This complex is suitable for patients of any age. The entire complex must be performed daily, since otherwise it will be almost impossible to achieve the desired effect from gymnastics.
Exercises for radiculitis of the lumbar spine are perhaps the most effective means to curb the disease, especially in the initial stage of its development. Principle It’s simple here: training strengthens the muscles, which in turn pulls the vertebrae together, preventing them from releasing pressure on the intervertebral discs. Thus, the discs are deprived of the opportunity to move to the side and pinch the lateral branches extending from the spinal cord, innervating the lower limbs.
These branches (roots) are called radixes in Latin. Hence the name – radiculitis. “It” is a suffix used in medicine to denote inflammation. That is, exactly what happens when the roots are injured by contacting vertebrae.
Gymnastics for radiculitis allows you not only to stop the development of the inflammatory process, but also to reduce it to nothing along with all the symptoms. It normalizes impaired blood circulation and stimulates the exchange of mineral salts, vitamins and other substances necessary to nourish the lumbar region. What , ultimately, relieves you of the most annoying companion of radiculitis - constant, excruciating pain.
Successful use of exercise therapy for radiculitis requires following certain rules. They include a number of fundamental provisions:
- The entire set of exercises must be agreed upon with a doctor. It is also necessary to consult with him in case of any difficulties during the course of treatment.
- If you have serious pain in the lower back, do not start exercising. Analgesics are also not advisable at the first stage. You need to focus only on your own capabilities.
- Start your workout with slow movements. Sharpness and increased loads are permissible only with sufficient preparation. This mode is the most physiological for the spine.
- All manifestations of pain should be alarming: it is necessary to either slow down the pace of exercise or consult a doctor if the pain does not subside. It can change the exercise configuration.
- The number of repetitions of each exercise should be increased in accordance with physical capabilities, aiming for a maximum by the end of the exercise therapy course.
- Conduct training regularly and purposefully: preferably several times a day, focusing all loads on the lumbar region. Only systematic training will lead to the desired goal.
- The room for gymnastics for radiculitis should be constantly ventilated, clothing should be spacious and not restrict movement.

- Be sure to read:
And the most important condition for achieving success is an extremely positive attitude.
Exercise therapy training course
The main task of this complex is to strengthen the muscular frame of the lumbar spine. This is achieved indirectly: all exercises are performed with tension in the abdominal muscles, which pulls the lower back towards itself.
Each exercise should be repeated from 5 to 15 times. At the initial stage of training, it is preferable to stick to the lower bar.
- The first exercise is performed on your back, in a lying position. Arms are extended along the hips with support on the heels, the feet of both legs are pulled back, and the palms of both hands are placed on the stomach. As you inhale, tighten your abs with a short breath-hold at maximum (the lower back should bend slightly). If pain occurs, you can perform a lighter version - without bending your knees.
- The starting position is the same: bend your legs slightly at the knees, resting on your feet. You need to lift your shoulders and shoulder blades off the floor, transferring the main load to the abs, and fix the position at maximum for a few seconds. Return to the starting point, relax. Repeat the exercises 5-15 times, according to the above regulations. A more complicated version - hands are placed behind the head when performing movements.
- The exercise is performed with support on your back, arms extended on the floor parallel to your hips. Bend your left leg at the knee joint, lift it above the floor, fix the position for 2-3 seconds. Straighten your leg, thereby increasing muscle tone in your abdomen. Do the usual number of repetitions and duplicate the same exercise with the right leg, then with both legs together. At the initial stage, 5 - 10 repetitions for each task are enough.
- Support on your back, arms along your hips, legs bent at the knees. Raise your left arm above the floor and place your palm on your right knee. Bend the right knee joint with abdominal tension, bringing it closer to the chest (the left hand should counteract this). Continue the “fight” for at least 10 seconds. Duplicate the exercise on the left leg.
- It is done on the floor in the “lying on your back” position. Legs and arms are extended parallel to each other. Raise your legs, lifting them off the floor by 30 centimeters, and fix the pose. Slowly, leaning on your abs, lower your legs to their original place. To complicate the task, you can put your hands behind your head.
- The starting position is similar to the previous one; for balance, place the palms of both hands on the floor and pull your knees towards your stomach. Imitate riding a bicycle with your feet: as if twisting the pedals (“twist” 10-15 times in the directions “away from you” and “toward you”). Continue for 1-3 minutes depending on the capabilities of the press.
- The load on the lumbar spine is carried out from the “lying” position. It is necessary to rest your palms on the floor, lift your outstretched legs from the floor by about 25-30 centimeters, and fix the position for a second. Spread to the side, and then cross your legs one over one in a horizontal plane, making a kind of “scissors”. To increase the load on the lower back, the exercise should be performed with your hands behind your head.
- Performed on the floor. Lie on your back, extend your arms parallel to your legs. From this position, bend your knees slightly, relying on the heels of both legs and the area of your shoulder blades, lift your lower back off the floor and try to reach the “bridge” (the arc should be as wide as possible). Hold the achieved position for at least 5 seconds. Return to the starting position, rest and repeat the task at least 10 times.
- From a position similar to the previous one, bend your legs pressed together, spread your arms to the sides, and rest your palms on the floor for balance. Cross your legs first to the right, then to the left from the projection of the torso with tension on the abs and lower back. The number of repetitions is standard.
- Lie on your stomach, place the backs of both hands under your chin. Raise your right and left legs up alternately, holding the maximum lift for about 10 seconds. 10-15 reps.
- It is also performed on the stomach. You should lie on the floor, spread your arms wide to the side until you feel tension in the lower back, “throw” your arms forward, as when swimming “breaststroke”, bring your hands to your shoulders, then spread your arms again. The number of repetitions is normal.
- Lie down with your back on the floor, stretch both arms straight forward. Then, with tension on the lumbar region, raise your right arm and left leg and hold the position for a few seconds. Relax and perform the same task with opposite limbs. A total of 5-15 times.
- Without changing the position of the body in the previous task, place your hands behind your back, clasp them using the “lock” method, raising your shoulders, bring them together at the shoulder blades, and relax. Mode – up to 15 repetitions.
- Strengthening the lateral muscles of the lower back. From the same position “on your back”, bend your legs, clasp your knees with your hands, clasping your fingers in a “lock”, pull your legs to your chest, tilt your torso alternately to one side in different directions from 5 to 15 times.
- Modification of the previous exercise: the body body, with knees tucked, rises up, then returns to place. Thus, the anterior and posterior muscles of the lower back, as well as the sacral spine, are strengthened.
- Be sure to read:
Systematic approach
In conclusion, it is worth repeating that exercise therapy for radiculitis of the lumbar spine gives lasting encouraging results only with systematic training. Largest The therapeutic effect is achieved by combining physical exercises with additional procedures, such as:
- Manual and physiotherapy;
- Acupuncture;
- Water aerobics;
- Forced stretching of the lower back on the simulator.

- Interesting read:
Hirudotherapy stimulates blood circulation well: leeches relieve swelling and suck out stagnant blood. Walking in the fresh air and a diet with a predominance of mineral salts and vitamins are beneficial. All this, taken together, is quite capable of stopping the disease and returning the victim to a normal, healthy life.
Physical therapy for radiculitis first mate.
Unlike drug treatment, which only helps eliminate the symptoms of exacerbation of the disease, physical exercise helps eliminate the very cause of sciatica.
It is important to understand all the rules for using physical therapy for radiculitis, when you can perform physical exercises so as not to worsen the health situation and what they should be.
Not all exercises are suitable for treating radiculitis.
It is necessary to use only complexes specially designed for this purpose, developed by specialists.
What is radiculitis, symptoms
Radiculitis affects the peripheral nervous system. It occurs due to pinching of the nerve roots of the spinal cord. At the same time, the latter are subject to an inflammatory process and can even be damaged due to serious pinching. This disease characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission.
During periods of exacerbation, severe pain occurs in the affected area of the spinal column.

The cause of exacerbations of radiculitis can be:
- stressful situations;
- hypothermia;
- passive lifestyle;
- playing sports;
- progressive osteochondrosis;
- hard physical labor;
- tumors of the spinal column;
- expanding osteophytes;
- deposited salts.
Depending on the location, the following types of radiculitis are distinguished::
| Cervical | Soreness appears in the neck and occipital region. The pain increases significantly with coughing and head movements. |
| Cervicobrachial | Pain occurs in the neck, shoulders and upper extremities. |
| Chest | Manifests itself as girdling pain in the sternum area. |
| Lumbosacral | Characterized by pain in the lumbar region, which can radiate to one of the lower extremities. |
Traditional treatment of sciatica
 Traditionally, sciatica is treated conservatively. The patient is prescribed:
Traditionally, sciatica is treated conservatively. The patient is prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ortofen, Ibuprofen);
- painkillers (Ketonal, Movalis);
- novocaine blockades;
- muscle relaxants (“Mydocalm”, “Sirdalud”);
- warming ointments based on bee or snake venom;
- B vitamins.
Severe damage to the intervertebral discs may require surgical treatment.
In addition to drug and surgical treatment for radiculitis, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to relieve the inflammatory process, as well as to accelerate tissue regeneration and have a warming effect. Manual therapy and visits to a massage room and exercise therapy room are also recommended.
Video: "Exercises for acute back pain"
The use of exercise therapy for radiculitis
Did you know that...
Next fact
Exercise therapy plays one of the most important roles in radiculitis.. Therapeutic physical exercises are prescribed for any type of radiculitis. Only the set of exercises itself can differ.
Exercise therapy is aimed at strengthening the spinal column, increasing its functionality by strengthening the surrounding muscle corset, including the abdominal muscles, which play an important role in maintaining the lumbar region of the spine.
Besides therapeutic exercises improve blood circulation, which has a positive effect on the condition of the spinal nerves, improving their nutrition and swelling of soft tissues, helping to eliminate existing swelling.
For radiculitis, all exercises should initially be performed in a gentle manner. Only gradually can you increase the intensity of physical activity. Exercises should be performed from simple to more complex.
 Exercises that involve a lying position must be performed on a hard, flat surface. Ideally, use a specially designed mat during classes.
Exercises that involve a lying position must be performed on a hard, flat surface. Ideally, use a specially designed mat during classes.
Physical therapy classes are not prescribed to patients:
- during the period of exacerbation of radiculitis (there is a high probability of only aggravating health problems);
- for cardiac pathologies;
- with intervertebral hernias, in which there is a possibility of damage to the spinal cord;
- with increased ESR;
- with an increase in body temperature.
Even if you do not fit into the category of patients for whom there are contraindications to exercise therapy, Before starting the exercises, it is still recommended to consult a specialist, which must give its approval for this method of treating radiculitis. In addition, exercise therapy is an excellent prevention of this disease, and also helps to recover faster after surgical treatment.
Video: "Gymnastics for acute radiculitis"
Exercise therapy for the treatment of radiculitis, technique
For cervical radiculitis, the following set of exercises is recommended::
- I.P. – standing, legs brought together. Bow your head towards your chest so that your chin touches the chest. In this position, make smooth movements of your head from left to right and vice versa, without lifting your chin from your chest. Repeat up to 15 times.
- I.P. – standing, feet together. Slowly move the back of your head back, almost touching it to your upper back. Stay in this position for at least 2 seconds and return to the starting position. Repeat 10-15 times.
- While standing, make circular movements with your head, without allowing strong deviations back (i.e. movements should be performed along the minor axis). Repeat at least 10 times.
- The fingers of both hands are clasped together at the back of the head. In this position, tilt your head forward, completely touching your chest. In the final position, completely relax and hold for about 10 seconds. Then return to the starting position. Repeat 15-20 head tilts.
- Standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, place your chin on your right hand, while clasping the back of your head with your left. In this position, make smooth movements with your head to the right side, holding at the end point for 20 seconds. Then return to the starting position. Repeat 15-20 times. Then change your hand and repeat the same manipulations, but only in the opposite direction.
For thoracic radiculitis, you can perform the following set of exercises in the starting position standing:
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart, bend both arms at the elbow joints at chest level. Raise your arms to the sides as you inhale, trying to bring your shoulder blades together and return to IP. on exhalation;
- Bend your arms at the elbow joints and place your hands on your shoulders. Alternately raise your left and right arms up so that they form a right angle with your shoulders and stay in this position for a few seconds. Then you can raise both hands together. It turns out: one lift - the left hand, the second lift - the right, the third lift - both hands together. Each position must be repeated at least 5 times;
- Bend both arms at the elbow joints. Raise your arms bent at the elbows up and back into IP, holding at the top point for 2-3 seconds;
- While lying on your stomach, alternately lift your left arm and left leg, and then your right arm and right leg. Lifting should be done while inhaling. There should be 8-10 lifts for each pair of limbs.
- Feet shoulder width apart. Swing alternately with each upper limb in the appropriate direction, i.e. left - to left, right - to right. Swings should not be sharp. Repeat 10-15 movements in each direction.
For lumbosacral radiculitis, the following exercises are recommended::
- In a standing position, spread your legs shoulder-width apart. Bend your arms at the elbows and place them on your lower back. Perform smooth bends alternately to the right and left, pausing at the bottom point for 3 seconds and returning to I.P. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, gently bend your body forward and backward., lingering at the bottom point for several seconds. Your hands should be on your lower back. Repeat at least 10 times.
- Standing, feet shoulder-width apart, arms in a free position on both sides of the body, bend back and forth. The tilt should be while inhaling, and you should try to reach the floor with your hands. At the lowest point, freeze for 2-3 seconds. Repeat 5-10 bends in each direction.
- Lying on your stomach, place your arms loosely on either side of your body. As you inhale, leaning on your forearms, simultaneously lift your head and shoulders up, holding at the top point for 2 seconds, then return to IP. Repeat at least 5-7 lifts.
- Lying on your stomach, clasp your hands behind your back. As you inhale, lift your head up, while bending in the chest area. At the top point, pause for 2-3 seconds, and then exhale, return to the starting position.

Conclusion
Exercise therapy plays an important role in the treatment of radiculitis. But you should not resort to it without consulting a specialist. All exercises must be performed under the supervision of an instructor, who will ensure that the exercises are performed correctly and will help prevent mistakes that could aggravate the health condition.
Exercise therapy is aimed not only at strengthening the spinal column, but also at strengthening the muscle corset surrounding it, as well as improving blood circulation. It is not always possible to resort to therapeutic exercises for radiculitis. Therefore, consultation with a doctor comes first. It will not be possible to completely cure radiculitis by resorting to exercise therapy alone, so treatment of the disease should be carried out comprehensively - you should not refuse drug treatment.
Exercises for lumbar radiculitis can be done only after acute symptoms have been relieved. You should start classes in consultation with your doctor. Premature resumption of physical activity can negatively affect the patient’s well-being.
The benefits of therapeutic exercises
Before starting exercise therapy for lumbosacral radiculitis, you should consult with a specialist in physical therapy. Indeed, for different diseases, the approach to exercise will be significantly different.
A specialist will help develop a set of exercises for radiculitis that can help strengthen the muscle frame and improve the patient’s condition. Thanks to regular exercises, microcirculation and metabolism in tissues are activated. Lymphatic drainage increases, and stagnation in the pathological focus is eliminated. Due to trained muscles, the functionality of the spinal column increases, which is very important for the active life of every person.
 Exercise therapy for lumbosacral radiculitis helps to increase the clearance between the vertebrae. This has a positive effect on the condition of the affected spinal nerves due to the fact that their compression and swelling are reduced. At the same time, due to increased blood flow, they receive more nutrients. As a result, the pain syndrome decreases and the range of movements increases.
Exercise therapy for lumbosacral radiculitis helps to increase the clearance between the vertebrae. This has a positive effect on the condition of the affected spinal nerves due to the fact that their compression and swelling are reduced. At the same time, due to increased blood flow, they receive more nutrients. As a result, the pain syndrome decreases and the range of movements increases.
An additional goal of daily exercise is to strengthen the abdominal muscles. This will help prevent excessive arching of the spine in the lumbar region.
Principles of exercise therapy
Physical therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. At least for the first few classes. As soon as the patient has learned all the rules for exercise therapy and remembers the necessary movements, he can continue gymnastics.
When developing individual exercises for the treatment of lumbosacral radiculitis, the doctor must take into account the patient’s condition and the stage of the disease, the presence of contraindications and concomitant diseases.
 Basic recommendations for carrying out exercise therapy:
Basic recommendations for carrying out exercise therapy:
- The first lessons should be short. The duration and intensity should be increased gradually.
- You need to start physical therapy with simple tasks, each time adding new movements and complicating them.
- Workouts should be varied and include a combination of different exercises.
- In the treatment of lumbosacral radiculitis, static and dynamic movements should be used.
- Charging should be carried out daily, without skipping. The duration of physical therapy is determined by the doctor, and in some cases the exercises must be continued throughout life.
- If severe pain occurs, you should immediately stop exercising and consult a doctor.
Exercise therapy for radiculitis of the transverse sacral spine is preferably carried out in a supine position, sitting or on all fours. These poses can relieve stress from the spine. It is also necessary to take care of a special rug or bedding. This will ensure the most comfortable position and even slight shock absorption. In some cases, it is advisable to use a lighter starting position. Its essence lies in the fact that when the patient lies on his back, a bolster or a blanket folded in several layers is placed under his feet. And if a person is lying on his stomach, a pillow is used under the stomach.
 Therapeutic exercises for radiculitis begin with exercises aimed at relaxing muscles. Further training will include a set of movements with which you can strengthen and strengthen the muscle frame.
Therapeutic exercises for radiculitis begin with exercises aimed at relaxing muscles. Further training will include a set of movements with which you can strengthen and strengthen the muscle frame.
When developing exercises for the lumbosacral region, the presence of pain must be taken into account. If it is present, loads on flexion and extension of the spine should be excluded. This can lead to the development of serious complications, such as increased intradiscal pressure, especially in the area of the L5-S1 vertebrae, which are the most vulnerable.
Examples of exercises
Before you start training, you need to gradually stretch. To do this, lie on a surface placed at an angle of 20–40° relative to the floor. It is necessary to provide support in the armpit area so that the person does not slide down. The duration of stretching ranges from 3 to 20 minutes. This manipulation will allow the intervertebral discs to separate slightly, thereby reducing the pressure on the pinched spinal nerve roots.
 Another way to do stretching is in a pool. As an option, you can try vertical traction, but this must be done very carefully and only under the supervision of a specialist.
Another way to do stretching is in a pool. As an option, you can try vertical traction, but this must be done very carefully and only under the supervision of a specialist.
To treat lumbosacral radiculitis, you must use the following exercises:
- Lie on the floor, bend your knees and place your hands on your stomach. Tighten the rectus abdominis muscles several times so that you can feel it with your hands. If the adopted position is uncomfortable or painful, you can spontaneously change it a little - straighten one limb or turn slightly on your side.
- Lying on your back with your legs extended, raise your upper body and stay in this position for 5-10 seconds. The exercise is performed about 10 times with intervals of 5-10 seconds for rest. During the first exercises for radiculitis, this movement can be done with outstretched arms; in the future, the task should be a little more complicated - clasp them in a lock behind the head.
- Lying on your back, bend one leg at the knee, lift it, extend it and after a few seconds smoothly lower it. All actions are carried out in the air with each limb in turn. In 1 session you should complete 5–10 approaches.
- From a similar starting position, you need to bend both legs at the knees, lift them above the floor and lower them. Repeat 7-10 times.
- The use of exercises “Bicycle”, “Scissors”, “Bridge” has a positive physical effect.
- Lie face down on the floor, place your hands under your chin. Lift each limb in turn and hold it in this position for 5-8 seconds.
- Lying on your stomach, you should perform “Breaststroke” - circular movements with your shoulders.
- From the starting position, lying on your stomach, clasp your hands behind your back and raise your upper body for a few seconds. In total you need to do about 10 movements.

Even though the first classes will be accompanied by very light loads, you should be prepared for the onset of soreness. There is no need to be afraid - this phenomenon will pass quickly, it indicates that the muscles are unprepared.
Other exercises in the treatment of lumbosacral radiculitis
After acute clinical symptoms have been relieved and the patient’s well-being has improved, in addition to physical therapy, you can go to yoga. The main thing is to find an experienced and competent instructor who can not only select the right exercises, but also determine the required intensity of the load.
Yoga will help you fully relax after a hard day at work, relieve emotional and physical stress, and will also provide effective assistance in the treatment of lumbosacral radiculitis.

Any workout begins with a gradual warming up of the muscles, thereby eliminating injuries and other damage. The movements are carried out slowly, their intensity and duration gradually increase.
By adopting special poses, you can effectively stretch the spine, increase the gap between the discs, and remove pressure from the roots of the spinal nerves. Correct body position ensures activation of all internal forces of the body, stimulation of the circulatory and neuromuscular systems. Energy information exchange is normalized, well-being and sleep improve. The most useful positions are triangle, fish, wheel pose.
 Breathing exercises show good results. Despite the fact that such actions do not have a direct effect on the spine, they effectively expand the chest and contribute to good oxygenation of the body. Thanks to this, bone, cartilage and muscle tissue are strengthened.
Breathing exercises show good results. Despite the fact that such actions do not have a direct effect on the spine, they effectively expand the chest and contribute to good oxygenation of the body. Thanks to this, bone, cartilage and muscle tissue are strengthened.
Proper breathing will help relieve pain in the lumbar spine and even restore its mobility. Regularly attending classes or doing the necessary exercises on your own will help relieve the inflammatory process and prevent recurrence of exacerbation.
The use of yoga and physical therapy for radiculitis is carried out according to the principle: comfortable position, smooth and gradual movements, complete relaxation.