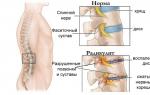
Medicines for vomiting and nausea. Anti-nausea tablets Anti-nausea injections for children
Antiemetic drugs
Antiemetics- drugs from different pharmacological groups that act on the vomiting center, trigger zone, and also have central and peripheral effects.
Antiemetic drugs include a large group of drugs that are different both in chemical structure and in characteristics.
mechanism of antiemetic action. Let's consider their classification.
- 1. Means, mainly blocking D 2 -dopamine receptors - haloperidol, thiethylperazine, chlorpromazine and etc.
- 2. Means, mainly blocking 5HT 3 -serotonin receptors - ondansetron, tropisetron and etc.
- 3. Drugs, mainly blocking D 2 -dopamine and 5HT 3 -serotonin receptors - metoclopramide.
- 4. Drugs, mainly blocking H1-histamine receptors - diphenhydramine, promethazine and etc.
- 5. Drugs, mainly blocking M-cholinergic receptors, - "Aeron" and etc.
- 6. Medicines local action - benzocaine.
Antiemetic drugs that primarily block O 2 -dopamine receptors located on the cell membrane of neurons in the trigger zone of the vomiting center, located at the bottom of the fourth ventricle of the brain, include the following: antipsychotics, How chlorpromazine(syn.: aminazine), haloperidol etc. As an antiemetic drug itself, a phenothiazine derivative is used in clinical practice - the drug thiethylperazine(syn.: torekan).
Unlike typical antipsychotic drugs, thiethylperazine does not have pronounced sedative activity, does not cause significant extrapyramidal disorders, and slightly potentiates the effect of hypnotics, narcotics and other psychotropic drugs. At the same time, thiethylperazine is significantly superior in antiemetic activity to typical antipsychotic drugs - phenothiazine derivatives, for example chlorpromazine.
In clinical practice, thiethylperazine is used to prevent and relieve vomiting in patients receiving radiation or chemotherapy for the treatment of malignant neoplasms, sea and air sickness, as well as vomiting during pregnancy.
Currently used as antiemetic drugs 5HT 3 -serotonin receptor blockers - ondasetron And tropisetron, which have proven effective in preventing and relieving vomiting caused by chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy for malignant neoplasms. Taking ondasetron and tropisetron allows you to significantly increase the dose of cytostatics.
In addition to selective blockers of D 2 -dopamine and 5HT 3 -serotonin receptors, they are used in clinical practice as an antiemetic drug metoclopramide (syn.: raglan, tserukal), the mechanism of action of which is based on the combined blockade of both types of receptors. The drug is used to prevent and relieve vomiting in violation of the diet, vomiting associated with anesthesia, caused by antibiotics, cytostatics, digitalis preparations, etc. There is evidence that the drug is effective for the treatment of dyspepsia (repeated vomiting, nausea) in severe cardiac patients.
The appearance of nausea and vomiting is possible when the normal physiological activity of the vestibular apparatus is disrupted, for example, during motion sickness while traveling in a car, on an airplane, seasickness, as well as in patients suffering from Meniere's syndrome (damage to the receptor apparatus of the inner ear, characterized, among other things, by attacks of sudden dizziness, nausea, vomiting). It is believed that in these cases the development of nausea and vomiting is associated with an increase in the activity of G 1 -histamine and/or M 1 -cholinoreceptors located on the cell membranes of neurons of the vomiting center.
To prevent nausea and vomiting resulting from disturbances in the activity of the vestibular apparatus, take non-selective blockers of G1-histamine receptors, for example drugs diphenhydramine(syn.: diphenhydramine), promethazine(syn.: diprazine) or combination drug aeron, which includes a non-selective blocker of M-cholinergic receptors - a drug scopolamine.
In addition to centrally acting drugs, they are used in clinical practice to prevent reflex vomiting. local anesthetics, for example a drug benzocaine(syn.: anesthesin). The latter, by blocking the sensitive receptors of the root of the tongue and/or the gastric mucosa, prevents the occurrence of reflex vomiting, for example, during bronchoscopy or irritation of the receptors of the gastric mucosa. The drug is effective for the prevention of vomiting during general anesthesia and instrumental diagnostics and/or therapeutic measures accompanied by irritation of the vomiting reflex centers.
Classification
These include m-anticholinergics, antihistamines, neuroleptics of the phenothiazine and butyrophenone group and etc.
Brief description of drugs
Ondansetron used for vomiting associated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer patients.
Metoclopramide has a regulating effect on the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract with nausea and vomiting of various origins, atony and hypotension (after gastrectomy).
Antiemetic drug Domperidone (Motilium) enhances gastric peristalsis and accelerates emptying.
Antiemetic Dimetpramide blocks chemoreceptors of the trigger zone, does not have a cumulative property.
Brief description of the pharmacological group. Antiemetic drugs are drugs that act on the vomiting center, trigger zone, and also have central and peripheral effects. These include m-anticholinergic drugs, antihistamines, neuroleptics of the phenothiazine and butyrophenone group.
Antiemetics (antiemetics)- These are drugs that suppress attacks of nausea and vomiting. Depending on the type, they block different pathogenetic components of the gag reflex.
Two areas in the brain are responsible for the occurrence of vomiting. The first is the vomiting center, which is activated by impulses coming from peripheral nerve cells. The second is the chemoreceptor trigger zone. It reacts to changes in blood composition, then sends signals to the vomiting center. Antiemetics suppress the activity of the receptors in this area and block the functioning of the vomiting center.
Serotonin receptor antagonists
Serotonin is one of the biologically active substances responsible for the transmission of electrochemical nerve impulses. Plays the role of a cellular mediator of inflammation. An increase in its concentration leads to vomiting. This group of drugs blocks serotonin receptors. Because of this, the release of serotonin is not suppressed, but the reaction in the form of vomiting does not occur. The main “point of application” is the 5-HT 3 receptors located in the gastrointestinal tract and the chemoreceptor trigger zone. Representatives:

Histamine H1 receptor blockers
Histamine is a mediator of inflammation. Mostly known as antiallergic drugs, but can also suppress vomiting. They block H 1 receptors of the chemoreceptor trigger zone and the vestibular analyzer, responsible for assessing the position of the body in space. Only 1st generation antihistamines are suitable as antiemetics because they penetrate the central nervous system. Representatives:

Anticholinergic
The main task of these drugs for vomiting is to prevent or suppress the interaction of acetylcholine (a neurotransmitter) and M-receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone. Anticholinergics have not only antiemetic, but also antispasmodic and sedative effects. Examples of drugs:

Dopamine antagonists
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that causes vomiting when trigger zone chemoreceptors are stimulated. Due to the activation of peripheral receptors, it increases the reflux of the food bolus (reverse reflux) from the duodenum into the stomach and from the stomach into the esophagus. There are several subgroups of drugs that block dopamine receptors. Representatives:

There are drugs that immediately block histamine, dopamine, and cholinergic receptors. One of these is Amitriptyline. It is most often used as an antidepressant.
Features of the use of antiemetic drugs
Antiemetics are selected in accordance with. There is no universal drug. Antiemetics can suppress discomfort, but do not affect the actual cause of vomiting. You can take them only after consulting a doctor.
For rotavirus in children
Dopamine receptor blockers are used. Domperidone (Motilium) is approved for infants. It normalizes gastrointestinal motility and eliminates vomiting.
During chemotherapy
 The effect of chemotherapy drugs is accompanied by a powerful release of serotonin. Therefore, preference is given to serotonin receptor antagonists: Ondansetron, Tropisetron, Granisetron. Their effect, if necessary, is enhanced by combining with dexamethasone.
The effect of chemotherapy drugs is accompanied by a powerful release of serotonin. Therefore, preference is given to serotonin receptor antagonists: Ondansetron, Tropisetron, Granisetron. Their effect, if necessary, is enhanced by combining with dexamethasone.
The second line drug is Metoclopramide. In high doses, it is able to block not only dopamine receptors, 5-HT 4, but 5-HT 3 receptors, which play a major role in the genesis of vomiting during chemotherapy.
In case of poisoning
Just like with rotavirus, dopamine receptor blockers are indicated. Metoclopramide and Domperidone have proven themselves well.
During pregnancy
Pyridoxine (vitamin B 6) and mint tablets are considered safe. They are used for mild nausea. If these drugs do not help, resort to the use of stronger antiemetics.
Dopamine receptor blockers are used with caution. Metoclopramide is allowed in the early stages. It cannot be used in the third trimester of pregnancy.
Second-line drugs are antihistamines. Pregnant women can be prescribed Bonin (Meclozine).
In case of intoxication
 For intoxication with alcohol and cardiac glycosides, dopamine receptor blockers are used: Metoclopramide, Domperidone.
For intoxication with alcohol and cardiac glycosides, dopamine receptor blockers are used: Metoclopramide, Domperidone.
For intoxication with synthetic drugs, dopamine receptor blockers (phenothiazines and butyrophenones) are also used: Chlorpromazine, Haloperidol.
With vomiting of vestibular origin
To stop vomiting during motion sickness, antihistamines are used. Meclozine (Bonin) is used.
Effective. The drug of choice is Aeron (based on scopolamine).
Dopamine receptor blockers (Metoclopramide) are ineffective for vestibular vomiting.
Contraindications
A general contraindication for all antiemetic drugs is hypersensitivity to any of its components. 5-HT 3 receptor blockers should not be prescribed to pregnant women, breastfeeding women and children under 2 years of age.
The exact restrictions on medications depend on the type of medication. For this reason, you should always read the annotation for each of them.
For histamine receptor blockers
For anticholinergics
For dopamine antagonists
Are there any side effects?
| Type of antiemetic | Side effects |
| Serotonin receptor blockers |
|
| Anticholinergic and antihistamine drugs of the 1st generation |
|
| Dopamine antagonists |
The last three side effects concern butyrophenones and phenothiazines. |
Vomiting is a protective reaction of the body. In this way, the stomach is freed from all toxic substances that have accumulated in it. It is not considered a separate disease, but rather a symptom that indicates that there is some kind of problem in the body. If vomiting in your case is just a temporary phenomenon, special tablets will help to cope with it.
, , , , , , , ,
Indications for use
Anti-vomiting pills are usually taken if it occurs after eating too much food, too much emotional stress or a stressful situation, taking certain medications (for example, cytostatics) for sea or air sickness, after radiation therapy or surgery. Before using any antiemetic, you need to pay attention that all drugs in this group have a different mechanism of action. That is, if you need to get rid of vomiting after overeating, you should take one pill, and for air sickness, another.
That is why, before using anti-vomiting pills, you need to determine the cause of its occurrence. If you cannot stop the unpleasant symptom, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Let's consider the pharmacodynamics of anti-vomiting tablets using the example of the popular drug "Cerucal".
As an effective antiemetic drug, Cerucal helps block serotonin and dopamine receptors. The main substance metoclopramide has peripheral and central effects. Thanks to the blockade of dopamine receptors in brain cells, the threshold of irritation of the center, which is responsible for the gag reflex, increases.
Thanks to its mechanism of action, Cerucal helps to quickly cope not only with vomiting and nausea, but also with hiccups. The action consists of reducing the motor activity of the esophagus, increasing the tone of the lower sphincter, rapid evacuation of the stomach, accelerating the movement of food through the small intestine without signs of diarrhea and normalizing the biliary function of the liver.
Let's look at the pharmacokinetics of anti-vomiting tablets using the popular drug "Cerucal" as an example.
The tablets are absorbed quite quickly immediately after they are ingested. Their bioavailability is up to 80%. Metabolism occurs in the liver. Half-life is eliminated within 3-5 hours. For chronic kidney disease, this process can take up to 14 hours. The drug is excreted unchanged through the kidneys within 1 day.
Using anti-vomiting tablets during pregnancy
During pregnancy, especially in the first weeks, nausea and vomiting are constant companions of a woman. Of course, they need to be treated. Today, pharmacies offer many different products that help cope with such an unpleasant condition, even during pregnancy.
For example, “Hofitol” is a fairly popular tablet for vomiting and nausea. It contains artichoke leaves and cynarin. But it also has contraindications: cholelithiasis, kidney and liver diseases, intolerance to components. Take Holifol 2-3 tablets three times a day.
Anesthesin is considered an equally popular remedy. This drug can be used not only during pregnancy, but also to treat vomiting in children.
Contraindications for use and side effects
The main contraindications to the use of anti-vomiting tablets are the following:
- Intolerance to their main components.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Children's age (rare).
- Chronic liver and kidney diseases.
- Bleeding of the gastrointestinal localization.
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum and ulcerative colitis.
Of course, like other medications, anti-vomiting tablets have their side effects. The most common are:
- Allergies (rash, hives, itching).
- Irritation, drowsiness, insomnia.
- Dryness and unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Agranulocytosis.
- Diarrhea or constipation.
If you notice side effects, you should immediately consult a doctor.
, , , , , , , ,
Names of anti-vomiting tablets
Metherazine. The drug is quite potent. It is often used to relieve vomiting and nausea caused by motion sickness. The active ingredient is prochlorperazine.
Use one tablet after meals three to four times a day. If after the first use all symptoms have disappeared, there is no need to reuse the drug.
The main side effects from the use of Meterazine are: drowsiness, dysmenorrhea, dry mouth, loss of appetite, allergies, swelling, agitation. These anti-vomiting tablets are contraindicated for: heart and vascular diseases, brain injuries, pregnancy and breastfeeding, breast cancer, glaucoma (especially angle-closure), epilepsy, old age, intolerance to components.
Aeron. Tablets that are used to prevent motion sickness and relieve symptoms such as vomiting. The active ingredients are: hyoscyamine and scopolamine.
The drug should be taken thirty minutes before a flight or trip on another type of transport. Take two tablets on an empty stomach. After one hour, you need to take another tablet. Sometimes Aeron is prescribed to reduce vomiting when the patient has a headache. It is not recommended to exceed the maximum dosage allowed for one day (four tablets).
This anti-vomiting remedy is not prescribed to patients with angle-closure glaucoma, chronic prostate diseases or intolerance to their components. Sometimes unpleasant side effects occur: thirst, dilated pupils, urinary retention, dizziness, accommodation paresis.
Diprazine. It is a popular sedative and antihistamine. Due to its calming effect on the central nervous system, it helps stop vomiting.
The drug is taken twice or three times a day (one tablet at a time) after eating. Very rarely, side effects occur after use: dry mouth, skin irritation, decreased blood pressure, drowsiness.
The product is completely contraindicated to be taken with alcohol. Also, vehicle drivers should not use the tablets. During pregnancy, you can take it after a doctor's prescription.
Cerucal
A popular antiemetic drug that helps block dopamine receptors. The active component of these tablets is considered to be metoclopramide hydrochloride monohydrate.

Take half an hour before eating. You should take the drug with a sufficient amount of water. Adults are recommended to take one tablet 3-4 times a day. Children can usually take half a tablet two to three times a day.
Cerucal is contraindicated at the beginning of pregnancy, in women who are breastfeeding, or with intolerance to its components. Common side effects from using the drug are: dizziness, migraines and headaches, severe fatigue, deterioration of emotional state, drowsiness, tinnitus, agranulocytosis, diarrhea, constipation.
, , , ,
Metoclopramide
An inexpensive and effective remedy for relieving severe vomiting, nausea and hiccups. Helps stimulate gastric peristalsis. Blocks dopamine receptors. The active ingredient is: metoclopramide hydrochloride monohydrate.

The average dosage of these anti-vomiting tablets is 1 tablet three to four times a day. If vomiting is very severe, the dose can be increased to 2 tablets.
Metoclopramide should not be used by pregnant women or while breastfeeding. Contraindications also include: bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, intestinal obstruction, epilepsy, intolerance to the components of the drug. Side effects from use are the following: diarrhea or constipation at the very beginning of therapy, drowsiness, severe fatigue, headache and migraine, akatasia, agranulocytosis, allergies.
Tablets for vomiting and nausea
Activated carbon. An excellent absorbent that helps cope with nausea and vomiting caused by overeating or taking medications.

The dosage depends on the patient's weight. Usually take up to 750 mg of activated carbon 3-4 times a day. The main side effects include: diarrhea, constipation, hypovitaminosis (with long-term use). Activated charcoal should not be used for bleeding in the stomach, or for patients with ulcers.
Kokkulin. This is a homeopathic medicine. The active ingredients are: cocculus indicus, tabacum, nux vomica, petroleum. The tablets must be dissolved in the mouth. Helps cope with nausea and vomiting during motion sickness.

Take two tablets three times a day 24 hours before your intended trip and on the same day. To treat vomiting that was not caused by motion sickness, dissolve two tablets until the normal state is completely restored (every hour).
Side effects: allergic reactions. Do not take if you are intolerant to the components of the drug or during lactase deficiency.
Tablets for vomiting and diarrhea
Polyphepan. This drug is of plant origin. It is derived from hydrolytic lignin. It has a detoxifying, enterosorbing, hypolipidemic, and antidiarrheal effect.

The tablets are taken an hour or an hour and a half before meals. The maximum daily dose for adults is up to 16 tablets (for children - 10 tablets). Therapy lasts no more than 7 days for acute diseases.
The main side effects are allergies and constipation. The drug should be taken with caution in patients with diabetes. It is contraindicated in case of intolerance to the main components.
Motilium. An excellent antiemetic that also helps relieve nausea and diarrhea. The main active ingredient is domperidone.

The average dosage is considered to be: 1-2 tablets 3-4 times a day. Contraindications for taking the drug are the following diseases: bleeding in the stomach, benign and malignant pituitary tumors, acute and chronic kidney and liver failure, intolerance to components, too low body weight (up to 35 kg), pregnancy, lactation.
Side effects include: intestinal spasms, agitation, convulsions, anaphylactic reactions, allergies, drowsiness.
Anti-vomiting tablets
Betagistine. The active ingredient of the drug is betahistine dihydrochloride. Usually this drug helps to cope with severe vomiting that was caused by motion sickness. To get an effective result, you need to take half a tablet 3 times a day a few days before your intended trip.

The drug is contraindicated in: pregnancy, breastfeeding, under the age of 18 years. Side effects from taking the drug may be: stool upset, allergic reactions.
Buscopan. The active ingredient in these anti-vomiting tablets is hyoscine butyl bromide. This drug is used to treat severe vomiting and nausea in gastrointestinal diseases.

The product should be taken three times a day, 1 tablet. The main side effects of the drug are: urinary retention, allergies, tachycardia, difficulty breathing. Buscopan is contraindicated in children under 6 years of age, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, and in patients with myasthenia gravis and megacolon.
Anti-vomiting tablets for children
Anestezin. The active ingredient of the drug is benzocaine. The main feature of this remedy is the fact that it can be taken even by small children to eliminate vomiting and nausea. The dosage is individual. It depends on the severity of the disease that caused the unpleasant symptom, as well as on the indications.

The main side effects from using this drug are allergic reactions. The product should not be taken if you are intolerant to its components.
Method of use and dosage of anti-vomiting tablets
The dosage of anti-vomiting tablets always depends on the chosen drug, the individual characteristics of the body and the severity of the patient’s condition. Some medications can be used without a doctor's recommendation. For additional information about dosage, you must carefully study the instructions for the drug.
Overdose
Sometimes, with an overdose of anti-vomiting tablets, side effects may increase. Patients often develop severe drowsiness, confusion, anxiety, irritation, and convulsions. If the poisoning was mild, then all symptoms of overdose disappear within 24 hours. If this does not happen, it is necessary to consult a doctor and establish constant monitoring of the patient’s vital organs.
See also aminazine, anesthesin, haloperidol, droperidol, peppermint tincture, neuleptil, prifinium bromide, mint tablets, chlorprothixene, etaprazine.
BROMOPride
Synonyms: Bimaral, Albex, Antemex, Bromil, Digezan, Emepride, Lemetic, Mepramid, Modulan, Opridan, Predicil, Viaben, Viadil, Anauzin, Emedian, Pridecil, etc.
Pharmachologic effect. Soothes hiccups and improves the tone of the digestive organs.
Indications for use. As an antiemetic.
Prescribed mainly for nausea and vomiting associated with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (decreased tone of the stomach and intestines, belching, flatulence - accumulation of gases in the intestines, etc.), for gastritis, dyskinesia (impaired mobility) of the biliary tract, etc.
Method of administration and dose. Take 1 capsule (10 mg) orally 3 times a day before meals; in more severe cases - 2 capsules 3 times a day.
Can be used in the form of suppositories (suppositories) 20 mg 1-2 times a day, as well as intramuscularly or intravenously 1 ampoule (10 mg) 1-2 times a day.
Side effect. In rare cases, headache, dizziness, weakness, and dry mouth are possible.
Contraindications. Pregnancy.
Release form. Capsules of 0.01 g (10 mg) in a package of 60 pieces; suppositories for children, 0.01 g (10 mg) and for adults, 0.02 g (20 mg); 0.5% solution in ampoules of 2 mg (10 mg per ampoule).
Storage conditions. In a place protected from light.
VOGALEN
Pharmachologic effect. Antiemetic. By acting on the vomiting center, it prevents nausea and vomiting of various origins.
Indications for use. Vomiting and nausea of any origin in adults, children and newborns.
Method of administration and dose. Adults are usually prescribed 5 to 20 mg (2-8 tablets) per day; for children, depending on age, in drops from 5 to 15 mg (50 or 150 drops) per day; for newborns - from 0.5 to 1 mg (5 or 6 drops) per day per 1 kg of body weight. Drops are recommended to be used 15-20 minutes before meals.
Release form. Tablets 2.5 mg; ampoules of 10 mg.
Storage conditions. List B.
DIMENHYDRINATE (Dimenhydrinatum)
Synonyms: Daedalon, Daedalon, Adrazin, .Anautin, Andramin, Antemin, Antivomit, Aviomarin, Chloranautin, Daldalon, Diphenhydramine teoclate, Dramamine, Dramil, Emedil, Marevit, Menhydrinate, Nauseal, Permigal, Teodramin, Travelin, Vertirosan, Vomidrin and others
Pharmachologic effect. Hi-receptor blocker. Shows pronounced antiemetic activity.
Indications for use. To prevent and relieve (relieve) the manifestations of seasickness and air sickness, with nausea and vomiting of various origins, with Meniere’s disease, etc.
Method of administration and dose. Prescribed orally (before meals), depending on the patient’s condition, 0.05-0.1 g (1-2 tablets) 4-6 times a day. To prevent air and sea sickness, 1-2 tablets are prescribed half an hour before boarding a plane or ship.
Side effect. Dry mouth, drowsiness, impaired accommodation (impaired visual perception). These phenomena are eliminated by reducing the dose.
Release form. Tablets of 0.05 g (50 mg) in a package of 10 pieces.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry place.
DIMETHPRAMIDE (Dimethpramidum)
Pharmachologic effect. Has an antiemetic effect.
Indications for use. For the prevention and relief (relief) of nausea and vomiting in the postoperative period, during radiation treatment and chemotherapy of cancer patients, etc.
Method of administration and dose. Prescribed orally (before meals) 0.02 g 2-3 times a day; intramuscularly - 1 ml of 2% solution 2-3 times a day.
Higher doses: when taken orally - 0.1 g per day, when administered intramuscularly - 5 ml of a 2% solution (0.1 g) per day.
Side effect. Allergic reactions are possible.
Contraindications. Hypersensitivity to the drug, pregnancy, breastfeeding.
Release form. Tablets 0.02 g (20 mg); 2% solution in ampoules of 1 ml (20 mg).
Storage conditions. List B. In a dark place at a temperature not exceeding +20 °C.
DIXAFEN (Dixaphenum)
Pharmachologic effect. Has an antiemetic effect and stimulates the cardiovascular system.
Indications for use. As an antiemetic.
Method of administration and dose. Administer 1 ml intramuscularly 1-2 times a day before meals.
Release form. An aqueous solution (bright orange) containing dimetpramide, caffeine and ephedrine in ampoules.
Storage conditions.
DIMETCARB (Dimetcarbum)
Pharmachologic effect. Has an antiemetic effect.
Indications for use. Used as an antiemetic to prevent and relieve (relieve) nausea and vomiting.
Method of administration and dose. 1 tablet 3-4 times a day before meals.
Side effects and contraindications are the same as for dimetpramide.
Release form. Film-coated tablets containing dimetpramide and sydnocarb.
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
DOMPERIDONE
Synonyms: Motilium, Cilroton, Euciton, Nauselin, Peridal, Peridon, etc.
Pharmachologic effect. It has an antiemetic effect, soothes hiccups and eliminates nausea in some cases. Has a regulating and normalizing effect on the motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract, which is associated with a blocking effect
on dopamine receptors (D2) of the gastrointestinal tract. The action is similar to metoclopramide. Unlike metoclopramide, it does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier (the barrier between blood and brain tissue) and does not cause extrapyramidal disorders (impaired coordination of movements with a decrease in their volume and tremors).
Indications for use. Domperidone is used for functional disorders of the gastroduodenal region (the junction of the stomach into the duodenum), hypotension (decreased smooth muscle tone) of the stomach, reflux esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus due to reflux of gastric contents). The drug alleviates dyspeptic symptoms (digestive disorders) associated with decreased gastric emptying. It is also used for vomiting caused by various reasons.
Method of administration and dose. Adults are prescribed 10 mg 3-4 times a day before meals. For severe nausea and vomiting, prescribe 20 mg 3-4 times a day. Children with a body weight of 20-30 kg are given "/2 tablets 2 times a day, over 30 kg - 1 tablet 2 times a day. Children can be prescribed a 1% solution orally, 1 drop per 1 kg of body weight 3-4 times per day or 2.5 ml of suspension for oral (oral) administration per 10 kg of body weight 3 times a day. The drug is recommended to be taken before meals. If necessary, the dose of the drug can be doubled. Rectally (into the rectum) adults are prescribed 2 -4 suppositories of 60 mg; children over 2 years old - 2-4 suppositories of 30 mg; children under 2 years of age - 2-4 suppositories of 10 mg.
Side effect. Possible dry mouth, headache, diarrhea (diarrhea), allergic reactions (skin rash, itching), spasms of the smooth muscles of the stomach.
Contraindications. Bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, mechanical intestinal obstruction, perforation (through defect) of the stomach or intestines, pregnancy, breastfeeding, hypersensitivity to the drug. The drug is not prescribed to newborns, infants and children weighing up to 20 kg. Domperidone should not be prescribed with anticholinergics (atropine, antispasmodic, platyphylline, etc.) due to the fact that the latter inhibit intestinal tone.
Release form. Tablets of 0.01 g (10 mg), film-coated, in a package of 50 pieces. Granules. Solution for oral use. Suspension in bottles. Suppositories of 60, 30 and 10 mg.
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
MECLOSINE
Synonyms: Meclozine hydrochloride, Bonin.
Pharmachologic effect. Meclozine has antihistamine and anticholinergic properties. The place and mechanism of action of meclozine for dizziness of various natures are not clearly defined. Pharmacological studies of other antihistamines have shown that a possible site of action is peripheral labyrinthine structures (formations of the inner ear containing receptors of the auditory and vestibular apparatus); it can be assumed that they are also the site of action of meclozine.
Indications for use. Prevention and symptomatic (alleviating the condition, but not eliminating the cause) treatment of nausea, vomiting and dizziness.
Method of administration and dose. For adults and children over 12 years of age, for the prevention and symptomatic treatment of nausea, vomiting and dizziness, a daily dose of 25-100 mg is prescribed in several doses depending on the clinical effect.
A single dose of 25-50 mg of the drug prevents the symptoms of motion sickness for about
24 hours. The initial dose should be taken at least 1 hour before travel to ensure absorption of the drug. Subsequently, the drug can be taken repeatedly every 24 hours if indicated during the trip.
For nausea and vomiting in pregnant women, the drug is usually effective in a daily dose of 25-50 mg.
For labyrinthine and vestibular disorders (in this case, diseases characterized by nausea, vomiting, dizziness, imbalance due to diseases of the receptor apparatus of the inner ear), the optimal dose is usually 25-100 mg per day, depending on the clinical effect.
Side effect. Drowsiness, dry mouth, fatigue, vomiting and, in rare cases, blurred vision may occur. Like all antihistamines, it can cause increased excitability in children.
Contraindications. Hypersensitivity to the drug. Patients with glaucoma (an eye disease accompanied by increased intraocular pressure) and with an enlarged prostate gland should take meclozine only as prescribed by a doctor. When prescribing meclozine to pregnant women, the possible risks and potential benefits of the drug should be weighed. Extensive and long-term experience with the use of meclozine in women experiencing nausea and vomiting during pregnancy has not revealed any teratogenic (causing disturbances in fetal development) effects associated with taking the drug.
Due to the possibility of developing drowsiness, you should take the drug with caution when driving a car or driving dangerous machinery.
Release form. Tablets containing 25 mg of meclosine hydrochloride, in a package of 10 pieces.
Storage conditions. In a dry, cool place.
METOCLOPRAMIDE (Metoclopramidum)
Synonyms: Metoclopramide hydrochloride, Raglan, Cerucal, Perinorm, Clometol, Bimaral, Comportan, Gastrobids, Imperial, Maxolon, Regastrol, Rimetin, Terperan, Viscal, Klopan, Emetizan, Legir, Maxeran, Metoclol, Moriperan, Nauzifar, Paspertin, Peraprin, Plastil, Pramin , Primperan, Primperil, Reliverin, etc.
Pharmachologic effect. Metoclopramide is a specific blocker of dopamine receptors, as well as serotonin receptors.
The drug has an antiemetic effect, soothes hiccups and, in addition, has a regulating effect on the functions of the gastrointestinal tract. The tone and motor activity of the digestive organs increases. Gastric secretion does not change. There are indications that the drug promotes the healing of stomach and duodenal ulcers.
Indications for use. Metoclopramide is used as an antiemetic for nausea, vomiting associated with anesthesia, radiation therapy, side effects of drugs (digitalis preparations, cytostatics /substances that inhibit cell division/, antibiotics, etc.), dietary disorders, etc.
It has no effect on vomiting of vestibular origin (caused by motion sickness).
In gastroenterological practice, the drug is also used in the complex treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers, gastritis, dyskinesia (impaired mobility) of the abdominal organs, postoperative paresis (decreased strength and/or range of motion) of the intestines, flatulence (accumulation of gases) and other diseases.
The therapeutic effect is associated with increased tone of the stomach and intestines, accelerated gastric emptying and
pylorus (the narrowed part of the stomach at the point of its transition to the duodenum), reducing hyperacid stasis (stopping the movement of food in the stomach due to acidification).
There is evidence of the effectiveness of metoclopramide in the treatment of dyspepsia (repeated vomiting, nausea) in severe cardiac patients (myocardial infarction, heart failure) and vomiting during pregnancy.
The drug has also found use as a means of facilitating and improving X-ray diagnosis of diseases of the stomach and small intestine.
There is evidence of the high effectiveness of metoclopramide for migraine and the successful use of the drug for Tourette's syndrome (generalized tics - involuntary twitching of the face - in children).
Method of administration and dose. Metoclopramide is used orally, and in severe cases parenterally (intramuscular or intravenous).
Adults are usually given 10 mg (1 tablet) orally 3 times a day (before meals). 1 ampoule (2 ml = 10 mg of the drug) is administered intramuscularly (or intravenously) 1-3 times a day. Children are prescribed in smaller doses according to age (children over 6 years old, 2-1 tablet 3 times a day).
The tablets are swallowed without chewing, washed down with a small amount of water.
For X-ray examination, adults are administered 1-2 ampoules (10-20 mg) intravenously or given orally (5-15 minutes before the start of the study) 15-30 mg.
Side effect. The drug is usually well tolerated. In rare cases, extrapyramidal disorders (impaired coordination of movements with a decrease in their volume and tremors), characteristic of parkinsonism, are possible. The antagonistic effect of metoclopramide on dopamine receptors in the brain appears to play a role in the mechanism of these side effects. To relieve these phenomena, caffeine is administered parenterally (see page 73).
Children under the age of 14 should prescribe the drug with caution due to possible side effects.
When taking the drug, drowsiness, tinnitus, and dry mouth are also possible. To reduce these phenomena, the drug is sometimes prescribed after meals.
Contraindications. When using the drug in the form of injections, the ability to drive cars and perform work that requires special concentration may be impaired.
Release form. Tablets of 10 mg in a package of 50 pieces; in ampoules of 2 ml (10 mg per ampoule) in a package of 10 pieces.
Storage conditions. In a place protected from light.
RODAVAN
A combination drug containing chlorphenoxamine hydrochloride, 8-chlorotheophylline and caffeine.
Pharmachologic effect. It has an antiemetic effect, affecting the vomiting center.
Indications for use. Prevention and treatment of nausea and vomiting during seasickness, air sickness, pregnancy, radiation sickness and chemotherapy; after anesthesia.
Method of administration and dose. For the prevention of seasickness and air sickness, adults are prescribed 1-2 tablets or 1 suppository 2 hours before departure. This dose can be repeated immediately after departure.
For treatment, 1 suppository into the rectum 3-4 times a day or 1-2 tablets 2-3 times a day.
Side effect. Dry mouth, dizziness, poor coordination. Possible decreased response.
Release form. Tablets composition: chlorphenoxamine hydrochloride - 20 mg, 8 chlortheophylline - 20 mg, caffeine -50 mg; suppositories for adults composition: chlorphenoxamine hydrochloride - 80 mg, 8-chlorotheophylline - 40 mg, caffeine - 100 mg; suppositories for children composition: chlorphenoxamine hydrochloride - 24 mg, 8-chlorotheophylline - 16 mg, caffeine - 20 mg.
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
THIETHYLPERAZINE (Thiethylperazinum)
Synonyms: Torekan, Thiethylperazine maleate, "Goresten, Tresten.
Pharmachologic effect. The drug is effective against vomiting of various origins. Under experimental conditions, it suppresses vomiting caused by stimulation of the vomiting center (apomorphine) and irritation of gastrointestinal tract receptors (copper sulfate). The mechanism of the antiemetic effect of thiethylperazine consists of a calming effect on the vomiting center and a simultaneous effect on the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the medulla oblongata.
Indications for use. Thiethylperazine is used to prevent and stop vomiting of various origins, including during radiation therapy and chemotherapy of malignant neoplasms, during surgical interventions, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, sea and air sickness, migraines, and vomiting of pregnant women. Positive results (cessation of nausea and vomiting, reduction or cessation of dizziness, nystagmus of involuntary movements of the eyeballs, gait disturbances) were noted in vestibular and coordination disorders associated with cerebrovascular disorders, vegetative-vascular dystonia, Meniere's disease.
Method of administration and dose. Thiethylperazine is prescribed orally, 1 tablet (6.5 mg) 1-3 times a day or 1 suppository (6.5 mg) is administered 2 times a day (morning and evening), in acute cases, 1-2 ml is used intramuscularly ( 6.5-13 mg) per day. The course of treatment continues if necessary for 2-4 weeks. To prevent postoperative vomiting, 1 ml (6.5 mg) is administered intramuscularly approximately half an hour before the end of the operation.
Side effect. The drug is usually well tolerated. Sometimes there is dry mouth and drowsiness. In rare cases (usually in children), extrapyramidal disorders (impaired coordination of movements with a decrease in their volume and tremors) may develop; therefore, it is not recommended to prescribe the drug to children under the age of 15 years.
Contraindications. The drug is contraindicated in cases of severe depression of the central nervous system, in a comatose (unconscious) state.
Release form. Dragee (6.5 mg each); suppositories (6.5 mg each); ampoules of 1 ml (6.5 mg).
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
Tropisetron
Synonyms: Novoban.
Pharmachologic effect. An antiemetic agent effective for vomiting caused by chemotherapy with anticancer drugs. The mechanism of action is associated with selective blocking of peripheral and central serotonin receptors.
Indications for use. Tropisterone is used to prevent nausea and vomiting during tumor chemotherapy.
Method of administration and dose. Prescribed to adults in the form of six-day courses at a daily dose of 0.005 g (5 mg). On day 1, it is administered intravenously shortly before the start of chemotherapy. From the 2nd to the 6th day, take the drug orally.
For intravenous infusion, the contents of one ampoule (5 ml containing 5 mg of tropisetron are equal to 5.64 mg of tropisetron hydrochloride) are diluted in 100 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution or 5% glucose solution; inject slowly. Orally administered in the form of capsules containing 5 mg of tropisetron.
Capsules are taken on an empty stomach (1 hour before breakfast) with water.
Side effect. The drug is usually well tolerated. Possible side effects: headache, dizziness, feeling tired, constipation or diarrhea; in patients with arterial hypertension (high blood pressure), blood pressure may increase; in rare cases, visual hallucinations (delusions, visions that acquire the character of reality) are possible.
Contraindications. Pregnancy, breastfeeding.
It should be taken into account that rifampicin, phenobarbital and other drugs that induce (increase) the activity of liver enzymes reduce the concentration of tropisetron in the blood plasma.
Release form. 0.1% solution in ampoules of 5 ml (5 mg of the drug in an ampoule) in a package of 5 pieces; capsules containing 5 mg of tropisetron.
Storage conditions. List B. In a place protected from light.
- How to stop vomiting
- When can medications be prescribed?
- Antiemetic drugs for children
- Other anti-vomiting agents
- Supporting events
Vomiting in a child can be caused by many reasons. In severe cases, doctors prescribe anti-vomiting injections. In isolated cases of such symptoms, the patient can be helped with home remedies. Despite the fears of many parents, doctors call vomiting a natural reflex of the body when the contents of the stomach are released through the digestive organs.
Vomiting is not an unexpected symptom. Usually, in front of it, the child’s skin turns pale, cold sweat appears, the process of salivation intensifies, the heartbeat quickens, and a loss of strength is observed. Vomit contains most of the leftover food that has not been digested by the stomach.
How to stop vomiting
To help a child stop vomiting, you must first change his position - lift the baby and turn his head to the side.
This must be done to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract. If vomiting has started recently and is not accompanied by diarrhea, fever and other symptoms, the child’s suffering can be alleviated by gastric lavage. This procedure, using a weak solution of potassium permanganate or simple boiled water, is carried out until the effluent water is clean.
During an attack of vomiting, first of all, it is necessary to replenish lost fluid and restore salt balance. For this purpose, children are recommended the products “Regidron”, “Orapit”, “Glucosolan”, which contain salt.
For kids, a solution of these drugs in the proportion of 1 powder per 1 liter of water is given every 5 minutes, a tablespoon. For nausea and vomiting, the child must be given absorbents - activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel. If the cause of vomiting is a viral infection, absorbent medications will not help. Severe vomiting must be stopped as quickly as possible and a doctor must be called immediately.
Return to contents
Anti-vomiting medications in children are prescribed only by the attending physician and only after studying the results of blood and vomit tests for infections or pathological processes in the body. Self-medication is strictly contraindicated. In addition, you cannot use antiemetic drugs without a doctor’s prescription, referring only to the instructions. Pediatricians draw the attention of parents to the side effects that may occur as a result of self-medication. The most common of them include:
- dizziness;
- convulsions;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- weakened vision;
- intestinal disorder;
- difficulty breathing.
It must be remembered that anti-vomiting drugs do not eliminate the underlying cause that caused this phenomenon. Such medications only help to stop the vomiting process for a while. Once the vomiting stops, the doctor is unable to assess the situation and diagnose the nature and amount of vomit.
Antiemetic drugs are also not supported by the fact that when the body is intoxicated, all harmful substances, while suppressing nausea and gag reflexes, remain in the body, which significantly aggravates the patient’s recovery process.
The doctor prescribes antiemetic drugs strictly individually - anti-vomiting injections or other drugs.
To ensure that the prescription is correct, the pediatrician examines the child, assesses the severity of his condition, and, if possible, determines the cause of vomiting. If acute attacks are associated with pathological phenomena in the digestive organs, head trauma, or neurological pathologies, the doctor decides in favor of prescribing antiemetics.
Return to contents
Common children's medications that a doctor can prescribe include those that have received all the necessary sanitary and pharmacological approvals. Today the most popular of them are:
- “Cerucal”. Available in the form of tablets, solutions for internal use, for intramuscular injections. The drug is prescribed to children over two years of age. The medicine has an effect that blocks the gag reflex, accelerates intestinal motility and facilitates the process of removing its contents. There are its analogues “Perinorm” and “Raglan” on sale.
- "Motilium". Available in the form of suspensions and tablets. The medicine is approved for use in children from infancy. Its main effect is to normalize intestinal motility, relieve symptoms of nausea, flatulence, and eliminate the gag reflex. Analogues of the drug are “Motilak”, “Domstal”.
- “But-spasm.” Available in tablets, syrup, intravenous and intramuscular injections. Prescribed from infancy. The drug has an active antispasmodic effect, eliminates pain, and normalizes the state of gastric juice. Today it has no analogues.
- "Atropine". It is commercially available in the form of tablets and injection solutions. The medicine eliminates the gag reflex and reduces the tone of the digestive organs. An analogue is “Atropine sulfate”.
- “Diacarb.” The drug is available in tablets. It can be given to infants and older children. The medicine has a diuretic property and reduces intracranial pressure, which often causes gag reflexes. Analog – “Acetazolamide”.
Return to contents
There are a number of drugs for general use that are prescribed to children (in pediatric dosages) and adults. The drug “Bromopride” is widely used, which has an antiemetic effect and increases hiccups. Prescribed for vomiting associated with disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. Contraindicated for pregnant women. Available for sale in suppositories, injection solutions, capsules.
The drug “Vogalen” helps stop nausea and stops the gag reflex. Prescribed from infancy. The drug can be purchased commercially in the form of tablets and ampoules for injection.
“Domperidone” is a drug with antiemetic properties that has a beneficial effect on the regulation and normalization of motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract. It is prescribed to children over two years of age in the form of injections, and for children under two years of age - in suppositories.
The drug “Meclozin” is used as a therapeutic and prophylactic agent that alleviates nausea and vomiting. It has a number of side effects, so it is prescribed to children from 12 years of age.
“Osetron” is a drug that relieves the symptoms of nausea and gag reflex that appear in children after chemotherapy. Prescribed intravenously to children over four years of age with a one-time injection.
Despite their effectiveness, all antiemetics have multiple contraindications and side effects. In this regard, it is recommended to strictly adhere to the treatment regimen prescribed by the pediatrician. In case of allergic or other negative manifestations, you should immediately consult a doctor and temporarily stop taking the prescribed drug. The doctor will decide to prescribe another medicine depending on the patient’s condition and, if necessary, will refer for repeated tests.
Return to contents
During the treatment process, doctors recommend switching to dietary nutrition, which should include the beneficial substances necessary for the body. To restore the liver damaged by toxin attack, the diet includes foods rich in protein (rabbit meat, veal, turkey meat, low-fat fish).
It is necessary to completely eliminate the consumption of fatty foods, which increase the load on the liver. Fast carbohydrates should also be excluded, and preference should be given to carbohydrates in the form of porridges. Coarse fiber, found in fresh vegetables and fruits, is contraindicated, as it can irritate the intestinal mucosa. You should definitely include fermented milk products in your diet. Doctors also recommend taking enzymes (pancreatin), microelements and vitamin preparations.
Cerucal - complete instructions
Tablets and solution for injection.
Pharmacological action of Cerucal
This drug can suppress the emetic effect, as well as normalize the tone of the gastrointestinal tract. The medicine contains metoclopramide, which has a therapeutic effect on the human body. The drug is able to block (selectively) serotonin and dopamine receptors, suppressing impulses from the chemoreceptors of the brain (brain), while preventing the increased sensitivity of visceral nerve cells responsible for the movement of impulses from the duodenum and pylorus to the medulla oblongata (in which the gag reflex is located), such thus preventing the appearance of the gag reflex. The drug cerucal - complete instructions is the best reference for patients.
As a result of the conduction of nerve impulses, as well as the effect of the action of the (parasympathetic) part of the autonomic nervous system, the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the upper ones, returns to normal. The action of the substance metaclopramide allows you to increase the tone of the muscles (smooth) of the gastrointestinal tract, while the time for movement of the mass of stomach contents into the intestines, especially into the duodenum, is significantly reduced, while its peristalsis improves.
This drug helps prevent the occurrence of reflux processes (pyloric and esophageal), as well as gastrostasis. The medicine normalizes the secretion of bile, reduces all symptoms associated with biliary dyskinesia, suppresses the manifestation of jaundice associated with disorders in the gallbladder (most often with stagnation of bile). The sphincter of Oddi is freed from spasms with normal general tone thanks to this remedy. The beneficial effect of the drug is known - suppression of gag reflexes, but in some cases its use may not be entirely effective, in particular if vomiting was caused by psychogenic factors and disorders of the vestibular apparatus.
Cerucal is prescribed both orally and in the form of injections at the discretion of the doctor, which of these treatment methods is most useful and productive in a particular situation. During oral administration of the drug, it is completely eliminated through the gastrointestinal tract, almost without residue. In plasma, the highest concentration of the substance included in the drug can be reached within half an hour or an hour from the moment of administration. The healing property reaches development after about 30 minutes, its persistence is observed within 12 hours from the moment of administration. The substance is eliminated from the body on average after 5 hours. Its excellent penetration through the biobarrier, including the hematoplacental and blood-brain barriers, was noted. The fact of penetration of the substance into breast milk was also revealed, which requires a special approach during breastfeeding. If the drug is administered intravenously, its activity is detected within two minutes, if administered intramuscularly, after an average of 12 minutes.
Cerucal indications
The medicine is prescribed for therapeutic purposes in case of disruption of the digestive organs, in particular their motor activity, as well as in case of irritable bowel syndrome, intestinal stenosis (functional), heartburn. In addition, this drug is prescribed during complex treatment of kidney and liver dysfunctions, for migraines, skull injuries with concussion, nausea, vomiting after taking various types of medications. Diabetics are prescribed Cerucal, the indications are quite consistent with eliminating the symptoms of intestinal paresis. It is also prescribed before diagnostic methods for examining the gastrointestinal tract, most often for x-ray examinations of the small intestine and stomach.
Cerucal application
This drug is prescribed both in tablets and in the form of injections. Cerucal solution is administered intramuscularly or slowly intravenously. Adults and adolescents from fourteen years of age are prescribed intravenous infusion or intramuscular injection three or four times a day, 2 ml, the dose of the drug per day is on average 25 mg (metoclopramide in its pure form), the dose at a time is no more than 10 mg.
The drug is administered intravenously over fifteen minutes at a rate of 2 mg/kg half an hour before the use of cytostatics, subsequently one and a half hours, three and a half, 5.5 and 8.5 hours after the cytostatic substance was administered.
Dosing of the drug is also possible according to a different scheme. The drug is administered intravenously in an amount of 0.5 mg/kg or 1 mg/kg over 60 minutes two hours before the administration of the cytostatic, after which a dose of 0.25 mg/kg or 0.5 mg/kg is administered over 60 minutes over a period of 24 hours after administration of the cytostatic. If cytostatic drugs are prescribed, Cerucal should be taken for the entire period of their prescription. Within fifteen minutes, cerucal is administered intravenously, diluted in 50 ml of infusion solution; it is permissible to dilute cerucal in a glucose solution (5%) or an isotonic NaCl solution. It is important to remember that mixing the cerucal solution with alkaline solutions (infusion) is unacceptable. In many cases, the drug cerucal will be quite useful; its use should be observed taking into account precautions.
Cerucal during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a complex physiological process that requires special caution regarding the use of medications, since this can be fraught with negative consequences and lead to damage to the vital organs of the fetus or provoke termination of pregnancy.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, it is not recommended to take Cerucal, as well as during breastfeeding, since the substance included in its composition can penetrate into milk and through the placental barrier, thereby affecting the body of the baby or developing fetus. The attending doctor, as a rule, prescribes cerucal during pregnancy during the first trimester other alternative treatment methods and replaces cerucal with other medications that do not have a negative effect on the fetus.
During pregnancy in the third and second trimesters, Cerucal can be prescribed only in exceptional cases, when this type of therapy exceeds the possible negative reactions to the body. In this case, you should not exceed the dose of the medicine recommended by experts; take Cerucal, strictly adhering to the prescription, at a certain time. It is important to know that self-medication, especially during pregnancy, is strictly prohibited due to possible undesirable consequences for both the pregnant woman and the developing fetus.
Cerucal for children
Teenagers over the age of fourteen can take Cerucal in doses recommended for adults. At the same time, you should not exceed the indicated doses and take the drug without consulting a doctor. Children under three years of age are not recommended to take cerucal, since the effect of the substance included in its composition can negatively affect the child’s health. With caution, you can prescribe the medicine to children over three years of age. Children from three to fourteen years old take the medicine at a dose of 0.1 mg per kilogram of total body weight, the highest daily dose is half a milligram per kilogram of body weight. The medicine is prescribed in cases where it is necessary to eliminate the state of nausea and suppress the gag reflex. Also, if vomiting is caused by the use of cytostatics, this remedy will be the most effective and will very quickly give a positive result.
Cerucal for children over three years of age is recommended both in tablets and injections. Dosages recommended by the doctor should not be exceeded, since in this way the opposite effect can be achieved instead of accelerating the positive effect. Children should take the medicine orally half an hour after meals. Usually the course of treatment is a month or a month and a half, but in some cases it increases to six months.
Tablets Cerucal
Cerucal in the form of tablets (50 pieces in one package) is prescribed to both adults and children over three years of age. Children over three years of age should be prescribed the drug at the rate of 0.1 mg per kilogram of weight. Children fourteen years of age and older take the tablets at the recommended dose for adults - 10 mg three or four times a day (as recommended by a doctor). Particular precautions must be taken by people suffering from kidney disease, in particular dysfunction of these organs. In this case, the dose of the drug is determined individually for each case. If possible, the drug is replaced by another, but if the use of metoclopramide is necessary for the best effect due to the severity of the body's condition due to dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and manifestations of gallbladder dyskinesia, the medicine is prescribed with caution. On average, the course of treatment is from 4 to 6 weeks.
Cerucal - tablets should be taken half an hour before meals with water. It is important to remember that alcoholic beverages are incompatible with most medications and can lead to severe complications, and therefore you should stop drinking alcohol during the course of treatment. You should not take the tablets with tea or milk, as the therapeutic effect may be significantly reduced. If the doctor has prescribed activated charcoal, you should also not take it less than an hour (one and a half) after taking cerucal, and you should also not take cerucal less than an hour after taking activated charcoal.
Cerucal injections
Cerucal is produced in liquid form for injection; each ampoule contains 2 ml of solution; there are only ten ampoules in a cardboard package.
If necessary, metoclopramide, which is contained in this drug, is administered intravenously with extreme caution, slowly or intramuscularly. Children under fourteen years of age are not given intravenous infusion. The doctor prescribes injections at his discretion; cerucal can be useful in any form. From the age of fourteen, adolescents and adult patients can receive a dose of the drug intravenously up to four times a day for some diseases, the dose of the drug is 2 ml, the daily dose does not exceed 25 mg, a single dose is up to 10 mg. The medicine is administered dropwise over 15 minutes (2 mg per kilogram of body weight), usually such treatment is prescribed while taking cytostatic drugs, and the generally accepted appropriate regimen for administering the substance is followed.
Cerucal side effects
During the use of the medicine, side effects from certain organ systems are possible, in particular: the nervous system, cardiovascular, hematopoietic, digestive and endocrine, and allergic reactions of the body are also possible. The following symptoms are observed:
- headache, fatigue, dizziness, tinnitus, depression, fear, neuroleptic syndrome;
- hypertension, hypotension, agranulocytosis, tachycardia;
- dry mouth, change in taste, constipation, loose stools;
- estrogenic hormonal disorders, menstrual irregularities, gynecomastia;
- urticaria, skin itching.
Adolescents and older adults are more likely to experience side effects than young and middle-aged adults, especially if they have kidney disease. If any side effects occur, you should immediately seek advice and help from your doctor.
Contraindications for the use of the medicine Cerucal
Despite the considerable number of beneficial properties, metoclopramide, which is part of cerucal, has a number of contraindications, which is associated with the effect of the substance on weakened organs susceptible to the pathological process. Contraindications include:
- pheochromocytoma;
- individual intolerance to metoclopramide;
- intestinal obstruction;
- sulfite intolerance;
- asthma of a bronchial nature;
- intestinal perforation, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract;
- prolactin-dependent tumors;
- seizures, epilepsy.
If a patient is found to have impaired renal function, the medicine should be prescribed with extreme caution and, if possible, replaced with another analogue that is less dangerous in this case.
Interaction of cerucal with other drugs
When using Cerucal with other drugs, a change in the rate of their absorption is observed, since the active substance - metoclopramide - helps to reduce the excretion of cimetidine, digoxin, but increases the absorption of ethanol, paracetamol and antibiotics. A decrease in the effectiveness of metoclopramide was noted during simultaneous use with anticholinergic drugs.
Under no circumstances should you take Cerucal with alcoholic beverages, as well as antipsychotics and sedatives. The breakdown of vitamin B1 is significantly accelerated by metoclopramide, while sympathomimetics, tricyclic antidepressants and MAO inhibitors change their activity under its influence. During a drug overdose, side effects such as convulsions, hyperkinesis, irritability, drowsiness, and an increase or decrease in blood pressure are possible.
Storage conditions for cerucal
The medicine must be stored at a temperature of 15 - 30 degrees Celsius in a dry place, protected from light. The shelf life is five years. The prepared solution for infusion is stored for up to 24 hours at a temperature of 18-22 degrees Celsius.
Cerucal price
The cost of the drug varies in the range of 90 rubles - 267 rubles. For a medicine like Cerucal, the price is quite reasonable.
Cerucal - reviews
- The doctor prescribed Cerucal for vomiting and nausea, he was very pleased with the effect, which came very quickly. I recommend.
- A month ago I became interested in the drug Cerucal, and read the reviews on the website. I suffer from gallbladder dyskinesia, and after taking the medicine I feel much better. I continue treatment.
- I have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, after taking Cerucal the relief is significant. The doctor did not recommend it to my wife because she has kidney problems.
- My child takes Cerucal as prescribed by the pediatrician. We are pleased with the result.
Similar instructions:
Acesol - instructions for use
Kokkulin - instructions, reviews
Metoclopramide: instructions, price, reviews
Granisetron: instructions, application, reviews
Tropisetron for nausea and vomiting
toshno.net
Cerucal - Polismed
We have collected frequently asked questions and prepared answers to themShe was treated in gastroenterology for pancreatitis. The doctor prescribed Cerucal, I would like to know why, because according to the instructions Cerucal is prescribed for vomiting and nausea. What else does it help with?
Response from the Medical College
Cerucal is a centrally acting antiemetic drug. It achieves its effect by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain. As a result, the motility of the upper gastrointestinal tract - esophagus, stomach, duodenum - increases. With pancreatitis, there is a very high probability of food stagnation in the stomach, which significantly impairs the efficiency of digestion, increasing the likelihood of vomiting. Prescribing Cerucal for pancreatitis improves the process of moving food through the digestive tract, reduces the risk of nausea and vomiting, and Cerucal improves the flow of bile, which also helps eliminate one of the causes of pancreatitis.
Can pregnant women take Cerucal?
Good afternoon, I need some advice. With the onset of pregnancy, I developed terrible toxicosis - any smell of food makes me sick. Can pregnant women take Cerucal in the first trimester to get rid of toxicosis? Katerina.
Response from the Medical College
Dear Katerina, unfortunately, no studies have been conducted on the safety of using Cerucal in pregnant women, so we cannot recommend Cerucal during pregnancy. We can only report that in experiments on mice and rabbits, exceeding the dose of Cerucal by 250 times did not cause negative consequences for the fetus.
How to give Cerucal to children?
Due to the fever, the child developed vomiting several times. There is no opportunity to visit a doctor now. Can a child be injected with Cerucal, and, if so, how much Cerucal should be injected if the child is one year old?
Response from the Medical College
In such a situation, when a child’s vomiting is associated with fever, we categorically do not recommend using Cerucal. Firstly, its use is allowed only from 2 years of age, since in younger children it can cause dyskinetic syndrome (an even worse digestive disorder). Secondly, vomiting in this situation is provoked by high temperature, so first aid means are NSAIDs. And thirdly, there is no need to self-medicate in potentially dangerous situations; in young children, vomiting can very quickly lead to dehydration.
What consequences can Cerucal cause?
When undergoing a course of chemotherapy, I was prescribed Cerucal as an antiemetic. However, the course of treatment is quite long. Isn’t this dangerous, and what consequences can lead to taking large doses of Cerucal?
Response from the Medical College
It is against the background of the administration of large doses of Cerucal during chemotherapy that the likelihood of developing side effects is highest. The most common of them are: drowsiness and extrapyramidal disorders (dizziness and hand tremors). All these consequences from taking the drug disappear on their own within 24 hours after stopping the drug. Caution should be exercised when prescribing and taking this drug for bronchial asthma, arterial hypertension and liver failure.
Is it necessary to dilute Cerucal and with what?
I have been prescribed Cerucal injections into the muscle. Should it be diluted with novocaine or water for injection to make it less painful?
Response from the Medical College
There is no need to dilute Cerucal when administered intramuscularly. The injection into the muscle is virtually painless. There is a point in dilution when administering the drug intravenously; in this case, it can be diluted with 5% glucose or isotonic sodium chloride solution.
What is better - tablets or Cerucal injections?
I was prescribed Cerucal in injections, but I am very afraid of them. Is it possible to replace them with tablets, is there a difference in effectiveness?
Response from the Medical College
The method of drug administration is determined by the attending physician, depending on the clinical situation. With severe vomiting, it is not always possible to take pills, since another attack of vomiting will cause the pill to “come back” back. In such cases, Cerucal will be effective as an injection against vomiting. If you are only worried about nausea, then you can get by with pills.
How to take Cerucal correctly?
We ran out of Cerucal tablets at home, but there were ampoules of the drug left. How can you stop vomiting in this case? Is it possible to drink an ampoule (a solution from it) instead of a tablet?
Response from the Medical College
Different dosage forms of drugs are intended for different clinical situations. Tablets are absorbed more slowly in the stomach and have a more prolonged effect, and when administered intravenously, the drug acts quickly. You can drink Cerucal solution from an ampoule, but where is the guarantee that the entire dose of the drug will reach the stomach? Part of it will remain in the ampoule, part - in the oral cavity. As a result, there may be no effect from taking the drug.
Is it possible to take Cerucal for alcohol poisoning?
One of the symptoms of a hangover is nausea (sometimes vomiting). How does Cerucal and alcohol combine? Can Cerucal be taken for alcohol poisoning or with a hangover?
Response from the Medical College
It is not recommended to take Cerucal simultaneously with alcoholic drinks. By stimulating gastric motility, the drug accelerates the entry of alcohol into the duodenum, where it is actively absorbed. As a result, the rate of onset of alcohol intoxication increases, and alcohol poisoning may increase. If you have a hangover, Cerucal can be taken, but there is no guarantee that vomiting caused by alcohol intoxication will be stopped, since at this time the body still contains breakdown products of alcohol, which cause nausea.
How long does it take for Cerucal to start working? When is Cerucal removed from the body?
If I take Cerucal tablets for nausea, how long does it take for it to start working? And when will its effect end?
Response from the Medical College
The effective concentration of the drug in the blood is achieved 1-2 hours after taking the tablet. The answer to the question of how long it takes for Cerucal to be removed from the body will help to provide knowledge about the pharmacodynamics of the drug. Its half-life is about 5 hours, after 24 hours the concentration in the blood is negligible, and after 72 hours the active substance is not detectable at all.
Is it possible to take Cerucal after surgery or chemotherapy?
I had surgery to remove my breasts and am now undergoing chemotherapy. How effective is Cerucal after surgery and chemotherapy - is it worth taking?
Response from the Medical College
This drug is quite effective for stopping post-anesthesia vomiting after many operations, including after cesarean section, after removal of the gallbladder. As an antiemetic, it is actively used directly during the infusion of cytostatic drugs, as well as after chemotherapy. The specific treatment regimen is selected by the attending physician.
Is it possible to take Cerucal simultaneously with other drugs?
Due to hypertension, I constantly take several medications (diuretics, beta blockers, statins). Is it possible to take Cerucal together with them?
Response from the Medical College
It is possible to combine Cerucal with the drugs you mentioned, but it is not advisable, since it can change their pharmacodynamics by accelerating gastric emptying. It is necessary to consult a clinical pharmacologist about the compatibility of this medicine with other drugs. The popular scheme of Cerucal with No-shpa in one syringe is generally an unacceptable combination.
polismed.ru
How to properly use cerucal for vomiting in children
Vomiting is a natural reaction of the body to the intake of harmful substances or pathogenic microorganisms. With the help of the gag reflex, the body self-cleanses. But sometimes vomiting becomes uncontrollable and can lead to dehydration. This condition is dangerous for people of any age, but young children who are low weight are especially affected. For severe vomiting, doctors prescribe various antiemetic drugs, one of them is Cerucal. Instructions for the use of cerucal for vomiting for children prescribe that it is allowed to be used even in children from 2 years of age, but only as prescribed by a pediatrician or infectious disease specialist.
Why does vomiting occur in children?
Vomiting in children occurs for various reasons. But in any case, the baby needs to get help quickly to prevent dehydration. The main causes of vomiting can be identified as follows: 
- Poisoning with low-quality food, medications or other toxic substances.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of an infectious nature.
- Congenital anomalies of the digestive organs or chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines.
- Weakness of the vestibular apparatus, which is accompanied by severe motion sickness in any transport.
- Binge eating.
- Excessive nervous tension.
Vomiting can also be caused by an allergy to a particular food product. Basically, this condition first manifests itself with hiccups and skin rashes, and then vomiting is added.
General characteristics of the drug
 Cerucal is a common antiemetic drug that can be used for nausea and vomiting in children. The active ingredient is metoclopramide. The medication enhances the motility of the digestive organs and stops the flow of signals between the nerve endings of the stomach and intestines to the brain, which is considered the center that activates the gag reflex. It is thanks to this that signals about indigestion do not reach the brain and nausea and vomiting do not occur.
Cerucal is a common antiemetic drug that can be used for nausea and vomiting in children. The active ingredient is metoclopramide. The medication enhances the motility of the digestive organs and stops the flow of signals between the nerve endings of the stomach and intestines to the brain, which is considered the center that activates the gag reflex. It is thanks to this that signals about indigestion do not reach the brain and nausea and vomiting do not occur.
The pharmaceutical industry produces anti-nausea tablets Cerucal and solution for injection. You cannot self-medicate, as the drug has many side effects, and the dosage can be chosen incorrectly. The drug is prescribed for disorders of the digestive system, which are manifested by excessive vomiting.
Illnesses in children that are accompanied by severe vomiting lead to severe dehydration in a matter of hours. In such cases, the only solution is cerucal, which it is advisable to use under the supervision of a doctor.
In what dose is Cerucal given to children?
The dosage of the drug is calculated based on the child’s body weight and the severity of the condition. In exceptional cases, the dose may be slightly increased, but this decision is made only by the attending physician: 
- Children from 2 to 14 years of age are prescribed the drug in a dosage of 0.1 mg of active substance per 1 kg of body weight, but the daily dose should not be more than 0.5 mg of metoclopramide per 1 kg of body weight. If the patient has chronic kidney disease, the volume of the drug is calculated by the doctor on an individual basis.
- Children over 14 years of age are allowed to increase the dose of the drug to 10 mg; they drink cerucal 3 times a day. The tablets are taken 30 minutes before meals, washed down with a sufficient amount of clean water. The full course of therapy often lasts up to one and a half months. The doctor can adjust the course of treatment based on test data and the general condition of the child.
Cerucal in ampoules is prescribed for children with vomiting in cases where gagging, nausea or hiccups need to be quickly stopped. Injections against nausea and vomiting for adolescents aged 14-18 years are given intramuscularly, at the rate of 1 ampoule up to three times a day. The dosage for injections for a child under 14 years of age is calculated by the doctor based on the weight of the small patient.
Cerucal cannot be stored in open ampoules. They are opened immediately before use, while observing all antiseptic rules. Store the medicine package in a cool, dark place out of reach of children.
Indications for use of the drug
Cerucal acts on the motility of the digestive organs, so it is prescribed for any disorders that are accompanied by persistent nausea and vomiting. It is indicated for the following diseases and conditions: 
- With severe nausea and uncontrollable vomiting, except in cases where such a condition is associated with weakness of the vestibular apparatus.
- In case of impaired motility of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, with dyskinesia of the bile ducts.
- For gastric paresis due to diabetes.
- In preparation for diagnostic manipulations on the digestive organs.
In addition, Cerucal tablets are prescribed to children for vomiting, when it is impossible to stop it by other means. This drug is usually used in a medical facility, but according to a doctor’s indications, therapy can also be done at home if the child is over 7 years old.
In young children and adolescents, the use of cerucal is limited by a number of contraindications, which must be taken into account when choosing a drug. These include the following diseases: 
- benign and malignant tumors that produce adrenaline in large quantities;
- chronic and acute intestinal diseases, including obstruction;
- prolactin-dependent tumors;
- history of epilepsy;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the intestine and duodenum;
- suspicion of bleeding in the digestive organs;
- individual intolerance to the substances included in the medication;
- spasms and nervous tics of the face;
- age of children under 2 years.
In special cases, cerucal is also prescribed to children under 2 years of age, after weighing all the risks. In this case, the attending physician calculates the dosage based on the age, weight and general condition of the sick child.
Cerucal has a lot of side effects that do not depend on the form of the medicine. The most common changes in health status include: 
- From the nervous system there may be increased fatigue, dizziness and tinnitus. There are also frequent complaints of nervous tics in children, which occur when taking the drug.
- On the part of the blood supply system, changes occur in the composition of the blood - the level of granulocytes, an important component of leukocytes, decreases.
- From the digestive system, there may be constipation or, conversely, diarrhea, as well as severe dryness of the oral mucosa.
- From the cardiovascular system, surges in blood pressure and increased heart rate are possible.
- On the part of the endocrine system, breast enlargement in boys and cycle failure in teenage girls are possible.
- On the part of the immune system, there may be allergies in the form of skin rashes and asthmatic attacks.
If any side effects occur while taking the drug, stop taking it and contact your doctor for treatment adjustments.
How to take Cerucal for poisoning
If a child is poisoned by poor-quality food products or medications, then through vomiting the body is cleansed and recovery occurs faster. In such cases, antiemetics should not be given immediately after the first bouts of vomiting, as this will inhibit the natural elimination of toxic substances. First, the child needs to be given first aid, which will be aimed at quickly removing toxic substances from the body. The emergency protocol is as follows: 
- The child's stomach is thoroughly washed with a large volume of water. You can take pure water or with the addition of potassium permanganate. Potassium permanganate is first dissolved in a small volume of water, and only then added to the total volume of water for rinsing.
- Give any adsorbents in a therapeutic dose. If activated carbon is used, it is first crushed into powder and diluted in a small volume of water, and then only given to the child.
- They do a cleansing enema, for which they take slightly salted water or chamomile decoction.
If all these measures do not help stop vomiting, then the use of antiemetic drugs, for example, cerucal, is indicated. In case of poisoning, you can drink Cerucal only after consulting a doctor.
Cerucal anti-vomiting injections are prescribed only in severe cases when the child cannot take pills due to vomiting. It is prohibited to prescribe or administer injections on your own, as this can lead to an overdose and serious consequences.
Drug overdose
An overdose of Cerucal can occur in the case of self-medication or an incorrectly calculated dose, when the doctor determines the weight of a small patient by eye. Another cause of overdose is improper storage of medications when they are stored in a place accessible to children. If a child takes too many Cerucal tablets, then it is necessary to urgently call a doctor or take the baby to the hospital on your own.
 Symptoms of overdose are quite specific; they can be distinguished by the following points:
Symptoms of overdose are quite specific; they can be distinguished by the following points:
- atypical drowsiness and confused consciousness appear;
- there is increased excitability and motor activity, which then develops into convulsions;
- the functioning of the heart is disrupted, which is manifested by instability of blood pressure, rapid heartbeat and high pulse.
If extrapyramidal disorders are observed during an overdose, then slow intravenous administration of an antidote, which is biperiden, is indicated. In this case, the child should be under constant medical supervision until all signs of overdose completely disappear.
How to prevent overdose
To avoid cerucal poisoning, it is enough to follow a number of simple rules: 
- Do not self-medicate, following the advice of relatives or neighbors. Any medications can only be taken if prescribed by a doctor.
- Do not leave medications within the reach of children. All medications must be stored in a special first aid kit or box that is locked with a key.
- Cerucal in ampoules is prescribed only by a doctor. The medicine can be injected only after 6-8 hours; during this period of time, the previous dose is almost completely eliminated from the body.
- Do not take expired medications. The active substance in such medications decomposes and forms toxic elements.
Even if a doctor prescribes cerucal for treatment, it is necessary to accurately tell him the patient’s weight. With a correctly calculated therapeutic dose, overdose is excluded.
Instead of cerucal, your doctor may prescribe other antiemetic drugs that have a similar effect. Despite the fact that cerucal is a highly effective antiemetic, it has a lot of contraindications and side effects, so if possible it is changed to other medications: 
- Motilium is an excellent replacement for Cerucal, especially since it is allowed to be prescribed to children from 1 year of age, and with constant supervision by a pediatrician, from birth. This anti-nausea and vomiting remedy for babies is sold in the form of a suspension with a pleasant taste, which makes treatment easier for babies. In addition, motilium helps get rid of flatulence, belching and a feeling of fullness in the abdomen. It is sometimes prescribed to infants for intestinal colic;
- No-spasm - prescribed for vomiting caused by functional disorders. This could be gastroenteritis, high intracranial pressure, or a consequence of radiation therapy. This medication can be given to children from the first days of life, but only under the supervision of a doctor and in accordance with the calculated dosage. No-spasm can be purchased in the form of a syrup for children and in the form of a solution for patients in the older age group.
All analogues have their limitations and side effects. Before you start taking it, you must carefully study the instructions.
What else can you do to stop vomiting in a child?
 When vomiting is caused by typical food poisoning and the child’s condition is satisfactory, then you can do without antiemetic drugs. In this case, traditional medicine recipes can help. To stop attacks of vomiting, children are given a decoction of peppermint or lemon balm. To prepare a medicinal decoction, you need to pour a tablespoon of crushed leaves into a glass of boiling water and leave in a thermos for about two hours. Then the broth is filtered and given to drink a tablespoon every half hour until the condition normalizes.
When vomiting is caused by typical food poisoning and the child’s condition is satisfactory, then you can do without antiemetic drugs. In this case, traditional medicine recipes can help. To stop attacks of vomiting, children are given a decoction of peppermint or lemon balm. To prepare a medicinal decoction, you need to pour a tablespoon of crushed leaves into a glass of boiling water and leave in a thermos for about two hours. Then the broth is filtered and given to drink a tablespoon every half hour until the condition normalizes.
A drink of honey and lemon will not only replenish fluid lost during vomiting, but will also regulate the balance of electrolytes in the body. This tasty drink has a tonic effect and quickly eliminates the urge to vomit. They use it often, but in small portions.
Before you try to stop vomiting, you need to understand what causes it. If this is poisoning with toxic substances, then you should not take Cerucal right away; you need to wait until the body is a little cleared of harmful substances.