Treatment of flat feet with a 100 guarantee. Treatment of flat feet
This verdict from doctors is upsetting for most parents: the child’s beautiful gait is at risk. Ah, if we were talking only about a cosmetic problem... Unfortunately, flattening of the arch of the foot is a serious and insidious pathology that can affect almost the entire musculoskeletal system. How dangerous is this disease? How to recognize it? And is it treatable?
Unfortunately, flat feet are one of the most common deviations from the norm in the development of the musculoskeletal system. Here are disappointing statistics: out of 1.5 million children in the city of Moscow, it was detected in 9 thousand children. And approximately 2 thousand young patients complain of pain in their legs. First of all, let's figure out what is meant by this pathology?
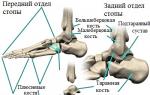
Flat feet is a deformation of the foot in which the arch of the foot is lowered (flattened). To better understand the nature of the disease, let's look at some anatomical features of the foot. In the process of evolution, it acquired a shape that allows it to evenly distribute body weight. The bones of the foot are connected to each other by strong interosseous ligaments (these are fibrous formations of connective tissue, presented in the form of a bundle connecting the bones) and form its arch, which provides shock absorption during walking and running. Convex arches are oriented in the longitudinal and transverse directions. Therefore, the foot of an adult normally rests on three points - the calcaneal tubercle, the head of the 1st metatarsal bone and the 5th metatarsal bone. There are two longitudinal and one transverse arches of the foot. The inner and outer arches form the longitudinal arch of the foot, and the front arch forms the transverse arch. Depending on their deformation, longitudinal and transverse flat feet are distinguished.
With longitudinal arches, the outer and inner arches of the foot are flattened, its length increases and almost the entire area of the sole is in contact with the floor.
With transverse, the transverse arch is flattened, the forefoot fan-shaped and rests on the heads of the five metatarsal bones.
All children under two years of age have a flat longitudinal arch of the foot. Experts consider this condition to be physiological, because the bone tissue in babies is soft and elastic. It contains few minerals, which give bones strength, and the muscular system is not well developed. When children begin to stand on their feet (at 7-9 months) and walk independently (at 10-12 months), the “fat pad”, which is located on the sole, under the skin, takes on the function of a shock absorber.
At 2-3 years, the bones gain a sufficient amount of minerals, the articular surfaces acquire normal shape, the ligaments become stronger, and muscle strength allows you to stay on your feet longer. The process of formation of the bones of the foot continues until approximately 5 or 6 years of age. Only during this period can we talk about the presence or absence of flat feet in a child.
When to go to the doctorPerhaps all parents understand that preventive examinations by specialists are not a whim of doctors, but a necessary measure. The main thing is not to miss the time to visit the doctor. An examination by an orthopedist is carried out:
Ideally, from this age on, you should visit an orthopedist with your child every year so as not to miss the development of flat feet. Parents need to be prepared for the fact that the orthopedist (if he doubts the final diagnosis) will refer the little patient for additional examination to a consultative and diagnostic center. If the child goes to kindergarten, this problem goes away by itself - preschool children in child care institutions are examined quite regularly. But if a child grows up at home until the 1st grade, parents should remember the date of the medical examination. Children who are found to have flat feet are monitored by an orthopedist until they are 14-15 years old. During this time, they undergo courses of physiotherapy, therapeutic massage, are sent to sanatorium-resort treatment, and, if necessary, special orthopedic shoes are made for them. |
If the diagnosis is confirmed
Most often, longitudinal flat feet occur in children. It can be congenital or acquired. The congenital form of the disease is rare and is a consequence of intrauterine malformations. It is already detected in the maternity hospital. In most cases, one foot is affected, but sometimes both are affected. This pathology is very noticeable in children: a convex sole and the forefoot “turned” outward. Treatment is carried out from the first days of the child’s life: the deformation is gradually corrected using plaster casts. If this does not help, they resort to surgery.
As for acquired longitudinal flatfoot, it can be:
- Traumatic.
Occurs after fractures of the bones of the foot and ankle. Partial or complete damage to the ligaments during such an injury, as well as the child’s prolonged stay in a plaster cast, contribute to the flattening of the arches of the feet.
- Paralytic.
Occurs due to disorders of the central or peripheral nervous systems (more often - consequences of polio 1).
- Static.
This is the most common form of pathology. It occurs due to overload with a significant increase in body weight, usually with obesity and endocrine disorders.
- Rachitic.
Occurs when there is excessive elasticity of the ligaments and weakening of the muscles of the arches of the foot. The cause may be a lack of vitamins and microelements - with 1 or general exhaustion, as well as with congenital pathology of connective tissue.
So, the foot turned out to be deformed. What happens in the body? The ligaments send “signals” to the nervous system about trouble in this “area”. In response, the muscles receive an “instruction” to enter into a “fight” with the deforming forces - that is, to tense up as they should. But they are not able to withstand such a load for a long time, so they quickly become exhausted, relax and stretch. And the deforming force continues to act now on the ligaments. Soon, stretching occurs in them (especially if there is a congenital pathology of the connective tissue), since without muscle support they cannot work for a long time. Now all the load falls on the bones. When they cannot stand it, deformation from compression begins. By this time, the ligaments finally “fail” and the deformation enters the final, irreversible phase. The gait loses its plasticity and smoothness. Children often complain of fatigue when walking, pain in the ankle joints or lower legs, and often in the lower back. Some cannot clearly identify where exactly they experience discomfort or pain, so they do not complain, but simply prefer calm, less active games. A deformity of the ankle joint appears (it is also called valgus or X-shaped). If one or more of these signs are present, consultation with an orthopedic doctor is necessary.
Sometimes a foot deformity can exist for many years (until adulthood) without showing itself in any way. But sooner or later, deterioration will occur, since the body’s compensatory capabilities are not limitless.
In a child 3 years old (but not earlier), an initial diagnosis of the pathology can be made using the most common method - plantography (footprint). This is easy to do at home. A blank sheet of paper is placed on the floor, and the baby stands on it with both feet. It is better that the soles are wet, then their clear imprint will remain on the paper. At the same time, the torso must be kept straight, legs together. The outline of the feet in this position is outlined with a pencil. Then a straight line is drawn perpendicular to the contour line, crossing the entire narrow part of the foot. The mildest degree of deformation is the first. Well, the heaviest and most serious is the third.
X-rays are not taken for children at this age. Firstly, the bones of the foot have not yet fully “matured”, the cartilage tissue is not visible on an x-ray and it is difficult to assess the true height of the longitudinal arch. And secondly, this diagnostic method is quite harmful for a child, so it is performed only for serious indications and more often after 9 years.
Only to eliminate severe pain is it permissible to use painkillers.
Treatment of flat feet
Unfortunately, one cannot count on complete relief from flat feet, especially with advanced pathology. But you need to be treated carefully, regularly and conscientiously. The earlier the signs of the disease are identified, the smaller the foot deformity, the more favorable the conditions for stopping the progression of flat feet and its correction.
At the initial stage, pain in the legs can be eliminated within 1-2 months through warm daily foot baths with sea salt, manual therapeutic massage and gymnastics. As for the baths, the requirements for them are simple: water temperature is +40-50 "C, the duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes, and the proportions of their components are indicated on the packaging and vary depending on the concentration of dry matter.
Self-massage will have a very beneficial effect - fortunately, there are many devices for it (special mats, rollers, balls). Exercises with them are performed arbitrarily (walking on a massage mat, rolling a massage roller with your feet, etc.). As a result, blood circulation improves and muscle tone normalizes. It is better to do gymnastics in the morning, when the muscles are not yet tired. It is better to show the technique and pace of exercises (see gymnastics) to the child by example. The room should not be stuffy or drafty, and the child should exercise in comfortable clothes that do not restrict his movements.
Therapeutic massage must be carried out by a certified specialist - an instructor in physical therapy and massage.
In the treatment of flat feet, physiotherapy (paraffin-ozokerite applications, electrophoresis, etc.) is often used, which improves metabolic processes and blood circulation in the tissues and indirectly strengthens the arches of the feet. Massage and physiotherapy are prescribed in courses, usually 10-15 procedures. It is advisable to conduct 2-3 courses per year.
Choosing shoesThe “culprit” of acquired flat feet may be incorrectly selected shoes. As soon as the child starts to stand up, it’s time to buy him his first boots. This usually occurs between 7-8 months. The criteria for “correct” children's shoes are clearly defined. The first shoes should:
|

"Magic" insoles
A special role in the treatment and prevention of progression of flat feet is given to orthopedic insoles, which are prescribed already at the first degree of pathology. They help relieve painful areas of the foot and correct identified deformities at the initial signs of flat feet. The height of the arches of the feet in the insoles depends on the degree of flattening. You need to invest them in street and indoor shoes to make life easier for the baby when he is on his feet for as long as possible. As the child grows, the shape and size of the insoles need to be changed. And here you cannot do without repeated consultations with an orthopedic doctor. It is best to purchase insoles from prosthetic and orthopedic companies, orthopedic centers, or order them individually.
Only in this case are such products guaranteed to meet the required standards. And one more thing: you shouldn’t use orthopedic insoles “just in case.” If you wear them constantly without an objective need, the arches of the feet will become relaxed, and flat feet can develop even in a child who is healthy from an orthopedic point of view.
If the baby has third degree longitudinal flatfoot, especially in combination with valgus deformity of the ankle joint, the matter will not be limited to insoles. He will have to “show off” in orthopedic shoes - boots with laces and rigid internal lateral support for the foot.
Gymnastics for flat feet Complex 1Starting position: sitting on a chair, feet on the floor. Curl your toes. Repeat 3-5 times without lifting your heels from the floor. Alternately lift your feet towards you (3-5 times). At the same time, turn your feet onto the outer edge (3-5 times). Alternately lift only the big toes (3-5 times). Lift all your toes one by one, with your feet slightly turned inward and do not lift your heels off the floor (3-5 times). Complex 2Starting position: sitting on a chair, feet on the floor. Run the big toe of your right foot along the front surface of the shin of your left leg from bottom to top (3-5 times). Repeat the same with the big toe of your left foot (3-5 times). You can complicate the exercise and try to pull the knee socks onto the shin of your left leg with the big toe of your right foot. Then change legs. Complex 3Starting position - sitting on a chair, one foot on the ball, the other on the floor. With your foot on the ball, swing it left - right, forward - back, (3-5) times. Change legs and repeat the exercise. Next, grab the ball with your feet and hold it suspended for several seconds, lower it to the floor, and then lift it again (3-5 times). Complex 4Starting position - sitting on a chair. You can put a piece of fabric, small objects (checkers, elements of a children's construction set, river pebbles, etc.), or a rolling pin under or near your feet. Task: gather fabric with your fingertips, grab and move small objects, roll a rolling pin, or with all your feet. Complex 5Starting position - standing. Stand on your toes (rise on your toes) (3-5 times). Turn your feet inward (3-5 times). Walk in place. Walk forward on the outer edges of your feet. Walk along the line. Complex 6Starting position - standing. Squat without lifting your heels from the floor (3-5 times). If possible, walk on rungs or walk on uneven, bumpy surfaces. You can also balance on a ball. (Attention! Adults must insure the child!) Complex 7Starting position - standing on a block placed on the floor. Squat on a bar (3-5 times). Stand on the block either on your right or left foot. In this case, the feet should be placed across and then along the bar. You can also walk several times with side steps across the block and walk along it. |
Complications
What are the complications of flat feet? Unfortunately, very different. First of all, this is a flattening of the transverse arch of the foot with subluxation of the 1st toe outward in adolescence. If the foot has been in an incorrect position for a long time, and especially if there is a valgus deformity of the ankle joint, this can lead to deformation in the joints of the foot and even to a change in the ratio of the articular surfaces of the knee and hip joints. This is accompanied by pain in the legs, especially in the evening, and a decrease in shock absorption functions leads to pain in the spine. In the future, this may lead to
Doctors diagnose “flat feet” when the foot loses its normal height and becomes flatter.
For a person, such changes threaten many problems, because due to disturbances in the position of the bones, depreciation during movement worsens.
Simply put, the smaller the bend, the greater the load on the joints and spine when moving. It is they who are responsible for absorbing shocks, which very quickly leads to wear and tear of fabrics and joints.
Flat feet are expressed in painful and unpleasant sensations in the legs - from the tips of the toes to the hips, as well as in the lower back.
As a rule, due to disturbances in the rise of the foot, first of all, the ankle, knee and hip joints begin to suffer, and the natural curvature of the spine is disrupted.
In both children and adults, flat feet can lead to the development of vascular complications, for example, varicose veins (in adults).
You should not let the development of the disease take its course - in the later stages, irreversible consequences are possible.
It is worth remembering that in particularly difficult cases, treating flat feet is impossible without the help of a surgeon.
Flat feet: main types of pathology
Disorders can be either congenital or acquired.
- IN first case The cause is an intrauterine malformation of bone tissue.
- In second case violations can result from an injury (foot or ankle fracture), heavy loads or previous diseases (rickets, polio, paralysis).
Doctors, based on the structural features of the foot, use a slightly different classification and distinguish three types of pathology:
- longitudinal, characterized by flattening of the longitudinal arch of the foot;
- transverse flatfoot, when the height of the transverse instep is reduced;
- combined – a case when the disease is complicated by two types of disorders.
To independently determine violations (especially the longitudinal type), just look at your own footprint - for example, on sand or loose earth. At home, just wet your feet and walk on newsprint.
An important condition is to stand straight, resting entirely on the entire surface of the foot. There is no need to roll, transfer weight from toe to heel and back.

Ideally, the footprint pattern should contain two separate parts - the heel and toe.
If your flatfoot is not strong, there will be a small bridge along the outer side.
The more pronounced the pathology, the thicker and larger it is.
Main causes of flat feet
Typically, a broken arch is the result of a combination of factors. First of all, this is a violation of muscle tone and ligament strength. Similar phenomena occur with low human activity, sedentary work and lack of regular physical exercise.
As a result, the foot simply does not work as nature intended, and under the influence of circumstances it begins to “sag” (longitudinal type of pathology).
The second reason is strong pressure on the lower limbs. This is possible if a person is overweight - in addition to strong pressure on the arch of the foot, extra pounds deteriorate the shock-absorbing properties and wear out the joints faster. High load can also occur during pregnancy - in this case, the weight of the fetus and amniotic fluid significantly increases the risk of disorders.
Of course, a hereditary factor cannot be ruled out: in some patients, doctors note a genetic predisposition, manifested in the form of weak ligaments and muscles of the foot, and less often, changes in bone tissue.
In everyday life, flat feet are “earned” by wearing incorrectly selected shoes:
- too tight
- in high heels,
- without anatomical insole.
In addition, injuries (bruises, fractures, sprains and tears of ligaments, damage to muscle fibers) and serious illnesses (primarily rickets and polio) can provoke the first stage of arch dysfunction.
Typical symptoms and manifestations of flat feet
The first warning sign should be pulling and pain in the lower extremities after exercise, walking (including in heels), and also at the end of the working day. Flat feet can also manifest themselves in the form of cramps and heaviness.
In the later stages, pain is felt not only in the lower legs, but also in the hip joints and lower back. Very often, such symptoms are accompanied by headaches and nervous breakdown.
At the first signs of deviations from the norm, you should consult an orthopedist.
Symptoms of flat feet are very easy to confuse with varicose veins, so a specialist should carry out the diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapeutic measures.
At home, it is very easy to make a mistake: for example, if the veins are dilated, massage may be contraindicated.
Degrees of flat feet: how pathology develops
Depending on the degree of change in the foot, doctors distinguish three degrees of flat feet.
Degree 1. It is very difficult to diagnose at home. A slight omission looks like a cosmetic defect, or is even accepted as a minor deviation from the norm. Pain occurs only as a result of prolonged exertion (for example, after a long hike) and quickly disappears after rest.
As a rule, the bones at this stage of the disease are not deformed, and the height of the foot can range from 25 to 35 mm.
Degree 2. Altitude violations are already noticeable to the eye. A person’s gait changes, the gait becomes heavy, and clubfoot often occurs. The pain when moving spreads all the way to the knee and does not go away for a long time.
The instep height can vary from 17 to 23 mm, and the surface of the foot is significantly deformed.


A. transverse flatfoot grade 1-2 b. longitudinal flatfoot 1-2 degrees
Degree 3. Disturbances in the structure of the foot entail a decrease in the functionality of the entire musculoskeletal system. Due to poor shock absorption when walking, pain occurs in the joints and muscles, and the knees and lower back begin to ache. The spine has to take on additional functions, resulting in an increased risk of diseases such as scoliosis, osteochondrosis, and herniated discs.
The pain in the third stage is acute and sharp, the ability to engage in physical activity is reduced to zero.
In order to simply move around, a person already needs special orthopedic shoes, individually tailored.
The surface of the foot is greatly deformed: calluses and corns appear, the toes change in length and shape, and the heel bends outward. Lifting height – less than 17 mm.
Treatment methods for flat feet
Doctors recommend correcting the instep defect as early as possible. The fact is that in adult patients it is impossible to return the foot to its natural state. Yes, there will be improvements, but you shouldn’t expect a full return of functionality.
The situation is different in children - at their age the bones and ligaments are mobile, and therefore flat feet can be completely cured.
For children, doctors select special correction methods that painlessly return the feet to the standard state.
Treatment of flat feet in adult patients
After diagnosis, you should not delay the prescribed procedures, since each passing year reduces the likelihood of a favorable outcome.
People cannot live without movement, and even a sedentary lifestyle puts stress on the feet. As a result, the deformation only intensifies every day.
All methods of improving the health of adult patients come down to reducing pain and restoring muscle tone and ligament strength.
- physical therapy (physical therapy),
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis, massage, magnetic therapy, phonophoresis),
- medicinal baths.
The instructions given by the doctor must be followed exactly, especially for individual exercises and massage. Regular exercise can strengthen ligaments and increase muscle tone in a short time.
In some cases, special orthopedic insoles are used to treat flat feet, which must be used at any opportunity.
Due to their shape, they evenly distribute a person’s weight and have a shock-absorbing effect when walking.
If we are talking about transverse flatfoot, surgical intervention cannot be avoided. During the operation, a small bone is removed, tendons are transferred, followed by osteotomy of the bones and correction of the deformity and arch.
This correction is quite traumatic, so more modern methods of intervention have been used recently.
In particular, the surgeon, through certain manipulations (corrective osteotomies), changes the transverse elevation and angle of convergence of the bones, which leads to a harmonious redistribution of the load on the feet and ligaments.
Recovery after surgery requires time and physical therapy. It is necessary to strengthen the muscle fibers and joints so that in the future the foot can work as naturally as possible.
For overweight patients, as well as people leading a sedentary lifestyle, doctors prescribe diets and additional activity. All this allows you to relieve stress from your legs and spine, and therefore improve your overall well-being.


A. appearance of the foot before surgery, b. foot after surgery.
What is the basis for treatment of flat feet in children?
Surgery in childhood is very rare. As a rule, pathology can be corrected with the help of insoles, shoes and various bandages (especially in the case of transverse flatfoot).
It is very important to pay attention to the tone of the muscle fibers - it is their weakness that, first of all, entails disturbances in the height of the foot.
Physiotherapy, therapeutic massages, exercise therapy, hardening, walking barefoot on stones, grass and other uneven surfaces - all this increases blood flow in the lower extremities, develops tendons and muscle tissue. Contrast baths have proven themselves well - dousing them with cold and warm water alternately.
It is very important to choose the right shoes for children - children should only walk on a flat, smooth floor with their shoes on!
The sooner parents notice the first symptoms of flat feet and contact an orthopedist, the higher the chance of full recovery. Progress is impossible without the attention and care of adults.


Prevention of flat feet in adults and children
Doctors say that preventing the occurrence of flat feet is much easier than curing it.
Therefore, adults who spend most of the day on their feet are advised to take regular breaks, during which they do special exercises.
In addition, while working, you should carefully monitor the position of your legs - your feet should be parallel, thereby evenly distributing your body weight.
Massage has a good preventive effect: you can knead the limbs with your hands or using special massage devices. If possible, it is recommended to remove your shoes and walk barefoot on the lawn, lawn, beach, paths and massage mat.
Particular attention should be paid to the choice of shoes: for the sake of fashion or momentary desires, you should not buy shoes that do not fit, are too loose or tight, and cause discomfort when worn.
A special orthopedic insole will be a useful acquisition - in addition to evenly distributing body weight across the foot, it also helps to improve its shock-absorbing properties.


In children, prevention must begin from the first days of life. Firstly, you should listen to the advice of doctors - preventing rickets, vaccinations against polio, as well as measures aimed at treating neurological diseases will help in the fight against flat feet.
As soon as the baby begins to walk, parents should purchase well-fitting shoes. The heel should be hard and high - it is better to save all kinds of straps for older children. It is necessary to have an orthopedic insole inside – it will help the baby’s foot develop correctly.
Whenever possible, children should be allowed to go barefoot - running on the lawn, beach, or street is very useful. On flat and smooth surfaces (for example, the floor in a house), it is better for children to walk in shoes. Recent studies have shown that the risk of developing flat feet is three times lower in those who regularly run barefoot.
For older children, special gymnastics are used: walking on their toes and heels, the outer and inner surfaces of the feet, jumping, raising their heels, rolling small balls or sticks. Simple exercises not only develop muscle fibers, but also strengthen ligaments and improve blood circulation.
Don't waste your time and money! Don't risk your health!
Contact a qualified orthopedist at the first symptoms of the disease. In our clinic we will help you quickly get rid of your illness.
This is a disease that manifests itself as a deformation of the shape of the foot.
The foot is a natural shock absorber that protects the body from shaking when walking and allows you to maintain balance when moving. The foot springs as it touches the ground; not the entire surface at once, but only part of it (reference points). As a result, a certain amount of empty space appears under the foot. When the load increases (for example, when taking a step), the foot sags a little, taking advantage of this volume; this allows you to avoid hard contact with the supporting surface, that is, a real blow.

When considering the shape of the foot, two arches are distinguished - longitudinal and transverse. Longitudinal arch- This is the curvature of the foot on the inside from the heel to the big toe joint. It is usually clearly visible. Transverse arch less noticeable. It is an arch at the base of the toes (where the metatarsals end). The position of the bones, in which both arches have a pronounced character, is fixed by the ligamentous-muscular apparatus. When the muscular-ligamentous apparatus is weakened, the normal shape of the foot is disrupted. The expression of the arches is lost, the foot settles and spreads out. This pathology is defined as flat feet.
What are flat feet like?
Deformation of the foot can lead to flattening of the longitudinal arch, in this case they speak of longitudinal flatfoot. Flatness of the forefoot is called transverse flatfoot. If the deformity affects both arches of the foot, combined flatfoot is diagnosed.
Flat feet may be congenital. In this case, improper development of the foot occurs due to intrauterine defects. This is a fairly rare occurrence. It happens much more often acquired flat feet, which can develop at any age.
Causes of flat feet
Acquired flatfoot is classified depending on the cause of the foot deformity. There are:
- traumatic flatfoot. Develops as a result of injury - fracture of the bones of the foot, ankle joint, damage to the connective tissues of the arch of the foot;
- paralytic flatfoot. Occurs as a result of paralysis of the muscles of the foot (for example, as a complication of the disease);
- rachitic flatfoot. With rickets in children, during a period of intensive growth, bone mineralization is disrupted: they become pliable and soft. This also applies to the bones of the foot, which are deformed under the weight of the child’s body;
- static flat feet. It occurs in cases where the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the foot cannot cope with the load placed on it. This is the most common type of flatfoot (more than 82% of all cases).
Static flatfoot is not caused by any disease. It can develop in both children and adults. The main factors contributing to its occurrence are the following:
- congenital ligament weakness;
- weakness of the muscles and ligaments of the foot, which developed as a result of low physical activity (sedentary, especially sedentary lifestyle);
- incorrectly chosen shoes. Women's shoes with high platforms or high heels are almost guaranteed to lead to flat feet;
- increased loads on the foot caused by life circumstances (professional activities associated with constant standing, etc.).
 Flat feet lead to a loss of shock-absorbing ability of the foot. As a result, the entire bone apparatus begins to experience harsh shocks when walking. The concussion is transmitted up the skeleton and reaches the brain. With severe flat feet, these excess loads affect various places, causing:
Flat feet lead to a loss of shock-absorbing ability of the foot. As a result, the entire bone apparatus begins to experience harsh shocks when walking. The concussion is transmitted up the skeleton and reaches the brain. With severe flat feet, these excess loads affect various places, causing:
- changes in gait and posture. The gait becomes heavy, “clubfooted”;
- foot diseases and foot pain;
- diseases of the knee joints (deforming, inflammation of the meniscus, laxity of the knee joint) and;
- diseases of the hip joint (coxarthrosis);
- diseases of the spine (herniated intervertebral discs, radiculitis) and back pain;
Symptoms of flat feet

Symptoms of flat feet depend on its type and stage of development of the disease.
In the development of longitudinal flatfoot, the following stages are distinguished: pre-disease, intermittent flatfoot, flatfoot of the I, II and III degrees of severity.
The first signs of flat feet
The following signs may indicate that you have flat feet:
- your shoes usually get worn down and worn out on the inside;
- when walking, your legs get tired quickly;
- When working on your feet, your legs get tired and swell by the end of the day. Swelling is usually observed in the ankle area. There may be seizures;
- You find that you need a larger shoe size because your feet have grown. Or your old shoes become too narrow.
Pre-disease stage
The pre-disease stage is characterized by the occurrence of leg fatigue and pain in the foot after prolonged static loads, that is, if you have to stand for a long time or walk a lot. Any discomfort or pain in the feet indicates a failure of the ligamentous apparatus. At the same time, the shape of the foot is not yet compromised.
Intermittent flat feet
At the stage of intermittent flatfoot, the foot loses its shape under load, but after rest the shape of the foot is restored.
Flat feet of the 1st degree
Flatfoot of the 1st degree is mild flatfoot. The foot deformity is minor. The longitudinal arch is preserved and has a height of at least 25 mm. When pressing on the foot, painful sensations may occur. The gait changes a little. When walking, fatigue quickly occurs. By evening, the foot may swell.
Flat feet of the third degree
Level III flatfoot is characterized by significant deformation of the foot. The longitudinal arch is practically absent. Severe pain makes even short walking difficult. Swelling of the feet and legs persists almost constantly. Maybe the strong ones are emerging.
Transverse flatfoot

The development of transverse flatfoot leads to the fact that the toes acquire a hammer-like shape. As a result of subsidence of the transverse arch, the metatarsal bones are displaced; the big toe deviates to the outside of the foot, and the head of the first metatarsal bone begins to protrude. Visually, it looks like a bone is growing at the base of the thumb. The higher the degree of transverse flatfoot, the greater the deviation of the big toe. There may be pain, swelling and redness in the area of the protruding bone. This indicates inflammation of the joint.
Methods for diagnosing flat feet
Diagnosis of flat feet is carried out by an orthopedic traumatologist. The degree of flatfoot is determined using instrumental research methods.
Treatment methods for flat feet
A complete cure for flat feet is possible only in childhood, since in children the bone and muscular-ligamentous apparatuses are still in the process of formation, and by eliminating the pathology, it is possible to achieve subsequent consolidation of the correct shape of the foot. In adulthood, we are only talking about some improvement in the situation and stopping the process of further deformation of the foot.
Contrary to the good old jokes about evading the army, flat feet are not a trivial ailment at all, but a serious orthopedic problem that can lead to many chronic diseases. Changes in the shape of the foot begin in childhood, so the sooner parents suspect something is wrong and show the child to the doctor, the better. Let's figure out where flat feet in children come from and how to deal with it.
0–3 years
At about a year old, an important event occurs in the baby’s life - the transition to a vertical position: the child takes his first steps, learning about the surrounding space. Up to 3 years of age, children’s feet are surrounded by a developed fat layer and visually have a flat surface, and the musculoskeletal system is not yet sufficiently developed. When the child begins to take his first steps, the fatty “pads” on the soles take on the function of springs. Gradually, the experience of independent active movements in space accumulates, and the foot takes on a normal appearance.
During this period, three pressure points form on the baby's foot, located on the heel, the area near the little toe and in the area under the big toe. These sections are fastened together by ligaments, muscles and tendons, so the entire structure forms three arches - two longitudinal (external and internal) and transverse. When walking, they act as shock absorbers, thanks to them the gait becomes light, and the legs get used to long hours of stress.
Now imagine that the arches of the foot - a kind of arches that pass between every two pressure points - sometimes, due to improper development of the musculoskeletal system (as well as some diseases), turn into straight lines and become flattened. It is no coincidence that when translated from English, flat feet are literally translated as “fallen arch.”
However, young children are not diagnosed with flat feet. However, if the child began to walk very early (before 9 months), suffered from rickets or has a hereditary predisposition to flat feet, the orthopedist can prescribe a prevention program that includes massage of the lower extremities, walking on an orthopedic rug and wearing orthopedic preventive shoes.
The purpose of such shoes is to develop the correct walking skill: the brain “remembers” the sequence of contraction and relaxation of muscles to perform a step, thanks to which the child continues to walk correctly even barefoot.
3–7 years
At this age, children develop the “adult” shape of the arches of the feet, and it is at this time that the orthopedist most often detects signs of pathology. Additional causes of flat feet in children of kindergarten age are excess weight, neurological and endocrine diseases. The disease can be suspected if the child places his legs oddly when walking, and after a long walk begins to limp.
The treatment and preventive program prescribed by the orthopedist involves the child performing special gymnastic exercises every day, swimming with fins, and sometimes physical therapy to improve muscle tone. In recent years, the technique of functional taping has become especially popular - gluing special adhesive tapes onto the patient’s body to tighten the skin and ease the load on joints and muscles. The prognosis for treatment among children of this age is favorable.
Simple rules of prevention will help prevent the development of flat feet in preschool children:
- Buy your child comfortable shoes that fit tightly;
- the height of the heel should not exceed 3 cm;
- allow your child to walk barefoot on uneven surfaces - bare ground, grass, sand;
- if possible, build a special path in the yard or at the dacha from wooden boards with many sections filled with various materials - gravel, cones, sand, etc.;
- the child’s diet should contain sufficient quantities of foods rich in calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D (they are important for the normal development of the musculoskeletal system);
- Make sure your child gets physical activity every day.
After 7 years
In first-graders, the arches of the feet have almost completed their development. With flat feet at this age, the first complications may appear in the form of pain in the legs and poor posture. This occurs due to the loss of the shock-absorbing function of the foot: all shocks during running and walking are transmitted to the upper joints and spine, damaging them. Over time, this can lead to arthrosis of the joints and early osteochondrosis of the spine.

How can you help a child with flat feet? Choose the right sports section for him with limited running and jumping exercises, buy orthopedic insoles (they will help avoid complications), and regularly enroll in courses of physical procedures indicated for this disease. Such measures will help prevent further deformation of the foot bones, rapid fatigue when walking and running, and poor posture.
Speaking about flat feet in children, I want to note two important aspects. Firstly, many parents do not take the disease seriously enough, and secondly, there is an overdiagnosis of this pathology among specialists. The first leads to a delayed start of treatment (let me remind you that the best results are observed when diagnosed at 3–7 years). The second is the pointless treatment of healthy feet.
It is extremely important to find an orthopedic doctor whom you are willing to trust and see your child with him at least once a year before starting school. This will help you find out about the problem in time and keep children's legs strong and healthy!
Nikolay Nigamadyanov
Photo istockphoto.com